SEO delivers significant results in eCommerce sites by reducing acquisition costs, building trust, enhancing brand awareness, and driving direct conversions while supporting other marketing channels.
Organic search accounts for 23.6% of eCommerce orders, according to SeoProfy, while Wolfgang Digital highlights that 33% of all eCommerce traffic comes from organic search.
With an impressive ROI of 1,600%, SEO outperforms paid search, as emphasized by Zipdo’s analysis. Ecommerce SEO is the practice of optimizin
Additionally, mobile optimization is critical, as 54.67% of global web traffic originates from mobile devices, according to Statista.
These insights underscore the importance of prioritizing SEO for sustainable growth and competitive success in Online Stores.
Discover 16 ecommerce seo marketing tips and best practices!
What is Ecommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO is the practice of optimizing an online store to increase its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The primary goal is to attract more organic traffic, boost user engagement, and drive higher sales. This involves optimizing key website elements such as product pages, site navigation, technical architecture, and content to align with search engine algorithms while ensuring a seamless and user-friendly shopping experience.
source: https://www.amazon.com/
7 Key Benefits of Ecommerce SEO
Ecommerce SEO is essential for building brand credibility and trust, lowering customer acquisition costs, improving user experience, boosting conversion rates, gaining a competitive edge, uncovering insights into customer behavior, and driving consistent organic traffic.
1. Building brand credibility and trust
Websites that rank higher in search results are seen as more trustworthy by users, strengthening brand reputation and fostering customer loyalty. According to a study by Moz, around 70% of users trust websites on the first page of search results more than those on later pages. Similarly, a survey by Search Engine Land found that 60% of consumers prefer organic search results over paid ads, underlining the trust that SEO helps to establish.
2. Reducing sales costs
SEO is a highly cost-effective strategy that substantially lowers customer acquisition expenses. A report by HubSpot reveals that inbound marketing methods, including SEO, can reduce these costs by up to 61% compared to traditional outbound strategies.
Furniture store example with cost per click:
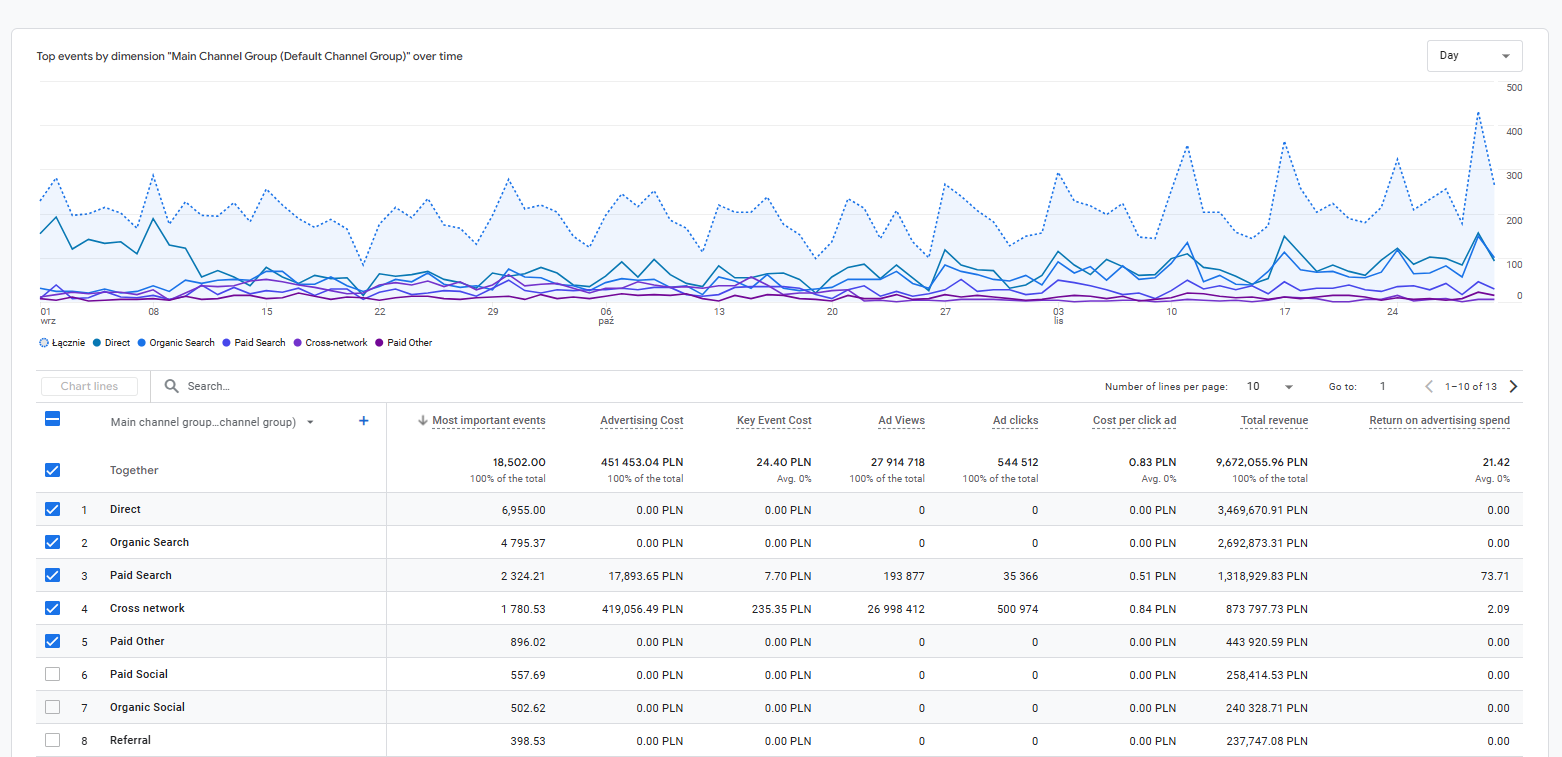
3. Enhancing user experience
Optimized websites offer superior user experiences by being faster, mobile-friendly, and secure. Research from Google shows that a 1-second delay in page load time can reduce conversions by 7%, emphasizing the critical impact of speed and usability on SEO performance.
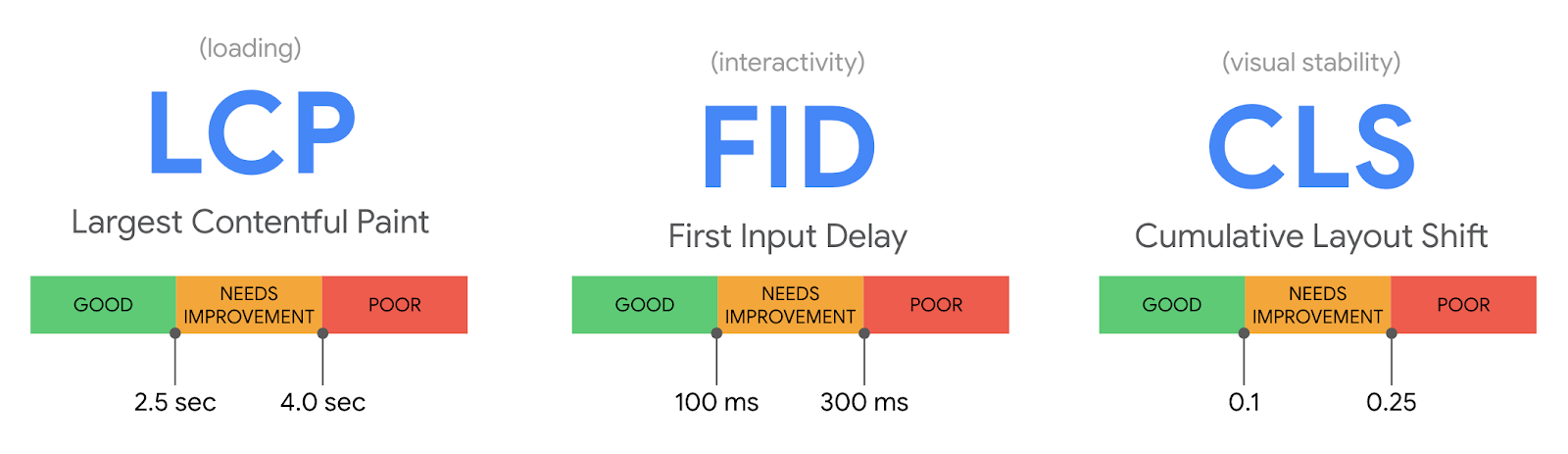
source: https://blog.chromium.org/
4. Increasing conversion rates
Prioritizing SEO can substantially improve conversion rates. According to a study by Econsultancy, SEO-driven leads achieve an impressive 14.6% conversion rate, compared to only 1.7% for outbound methods such as print advertising.
5. Gaining a competitive advantage
Focusing on SEO provides businesses with a significant competitive advantage. A report by Ahrefs reveals that over 90% of web pages receive no organic traffic from Google, highlighting a widespread lack of optimization among competitors. This creates a strategic opportunity for businesses that prioritize SEO to dominate search rankings and capture valuable organic traffic.
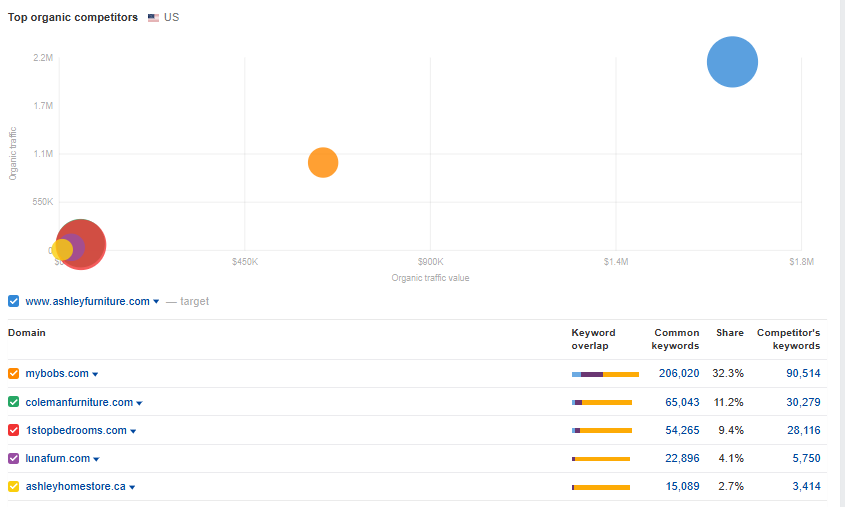
6. Providing insights into customer behavior
SEO tools such as Google Analytics, Ahrefs, and SEMrush offer valuable insights into customer behavior and market demand. By analyzing search query volumes across different countries and languages, these tools help businesses identify high-demand products and pinpoint the best markets to target, guiding decisions on what to sell and where.
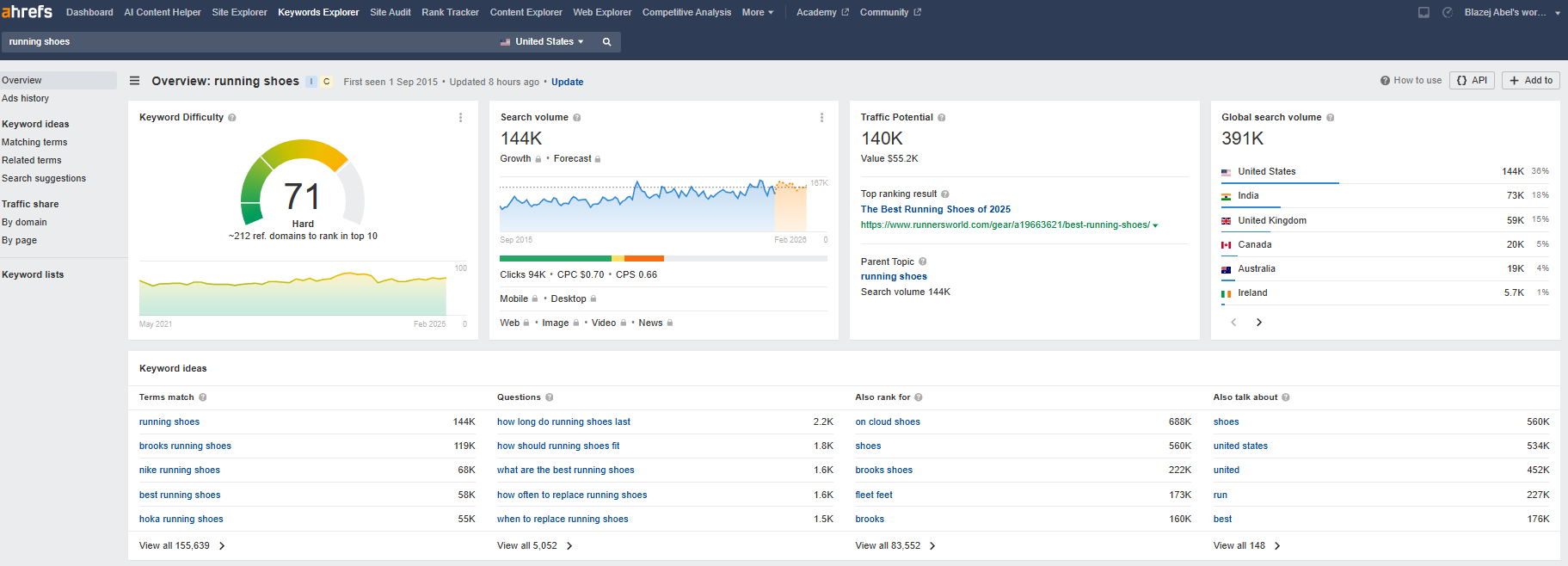
7. Driving organic traffic
Organic search is the leading driver of website traffic. A study by BrightEdge reveals that organic search contributes approximately 53% of all website traffic, underscoring the vital role of SEO in attracting high-quality visitors.
Ecommerce SEO integrates trust-building, cost efficiency, and strategic insights, making it an essential tool for businesses seeking long-term growth and market leadership.
16 Tips To Improve SEO Strategies for ECommerce
Discover 16 practical e-commerce SEO strategies, including competitor analysis, keyword research, internal linking, mobile optimization, and more. Each tip is crafted to help your online store rank higher, attract organic traffic, and boost conversions effectively.
These insights blend technical expertise with practical applications, empowering you to optimize your site’s performance, build topical authority, and deliver value to both users and search engines.
1. Analyze Your SEO Competitors
Competitor analysis is the first step to building a superior content strategy. By studying how your competitors publish, update, and structure content, you can identify gaps and create a topical map that outranks them in both depth and relevance.
How to Perform an SEO Competitor Analysis in Ecommerce?
To perform an effective SEO competitive analysis, follow these four steps:
Scrape their sitemap → Extract key data → Analyze using tools like Ahrefs → Build a stronger topical map.
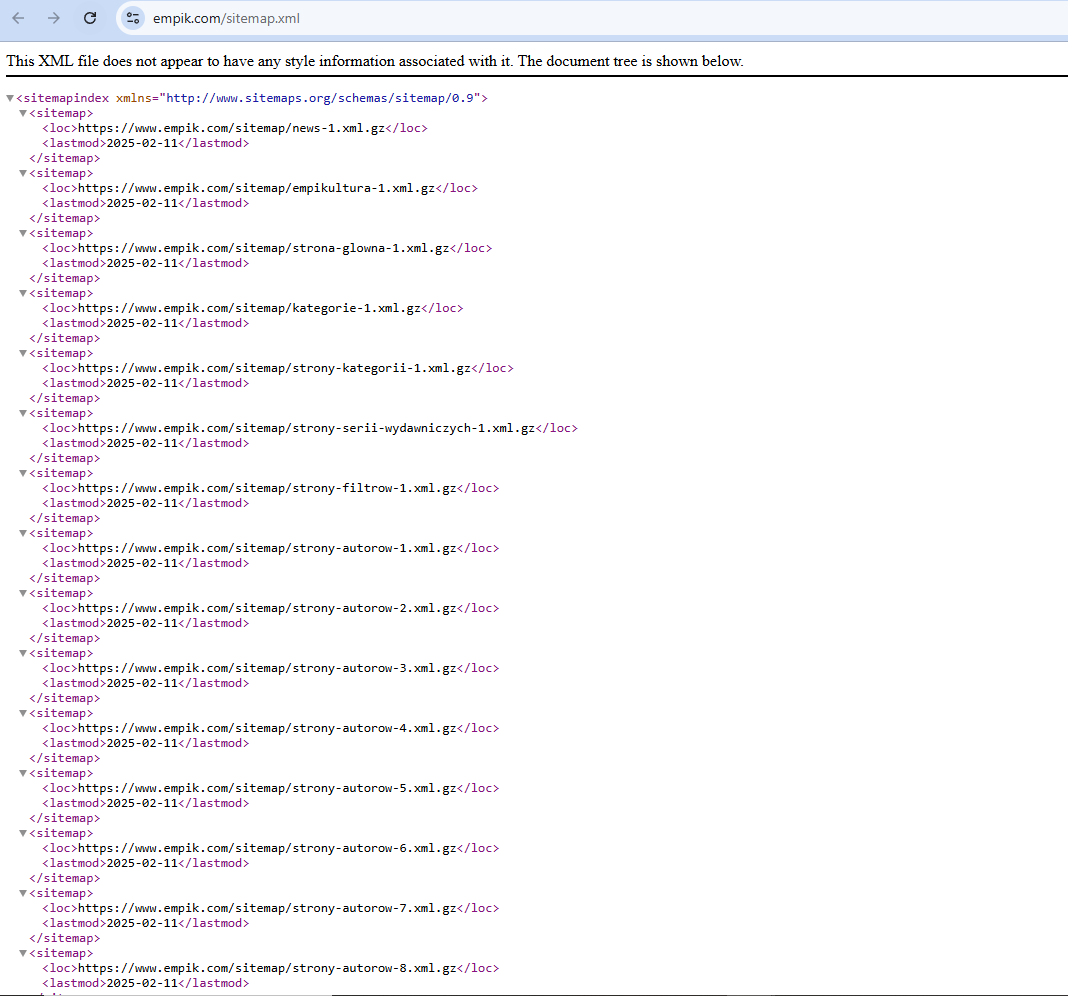
a) Scrape Their Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on a website, providing insight into their content strategy. By scraping your competitor’s sitemap, you can gather information on:
- Publishing Frequency: How often they publish new content.
Example: Competitor publishes three blog posts weekly, you should publish 4, to become topical authority you have to gather search engine attention by publish more and updating more than your competitors. - Content Updates: How regularly they refresh existing pages.
Example: Competitor updates their cornerstone articles every quarter to maintain relevance. Update yours more frequently. Remember, the freshness signal lasts for 6 months according to Google and Yandex leaks. - Volume: The total number of pages they’ve created.
Example: Competitor has 1,000+ indexed pages, signaling comprehensive niche coverage. Create a more compressed topical map to reduce indexing costs and improve ranking efficiency. If they have 10 articles on running shoes, consider consolidating into 7 to avoid keyword cannibalization, or go deeper with 15 for better coverage. When building a topical map, always aim to cover topics either more broadly or in greater depth than your competitor.
Where to Find Sitemaps:
Most websites list their sitemap at:
https://domain-name.com/sitemap.xml
Practical Example: https://www.empik.com/sitemap.xml
b) Use Tools Like Ahrefs for Advanced Insights
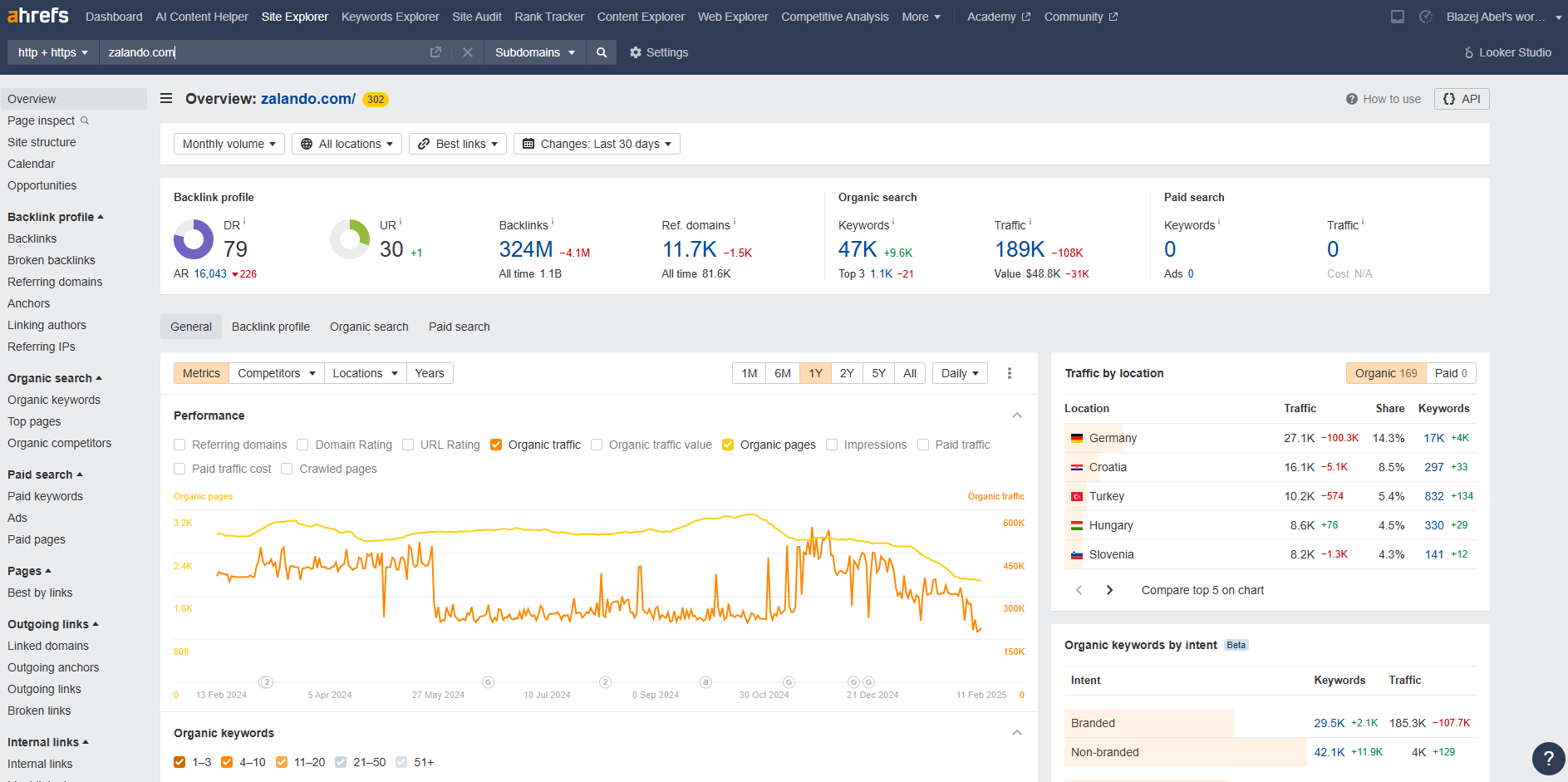
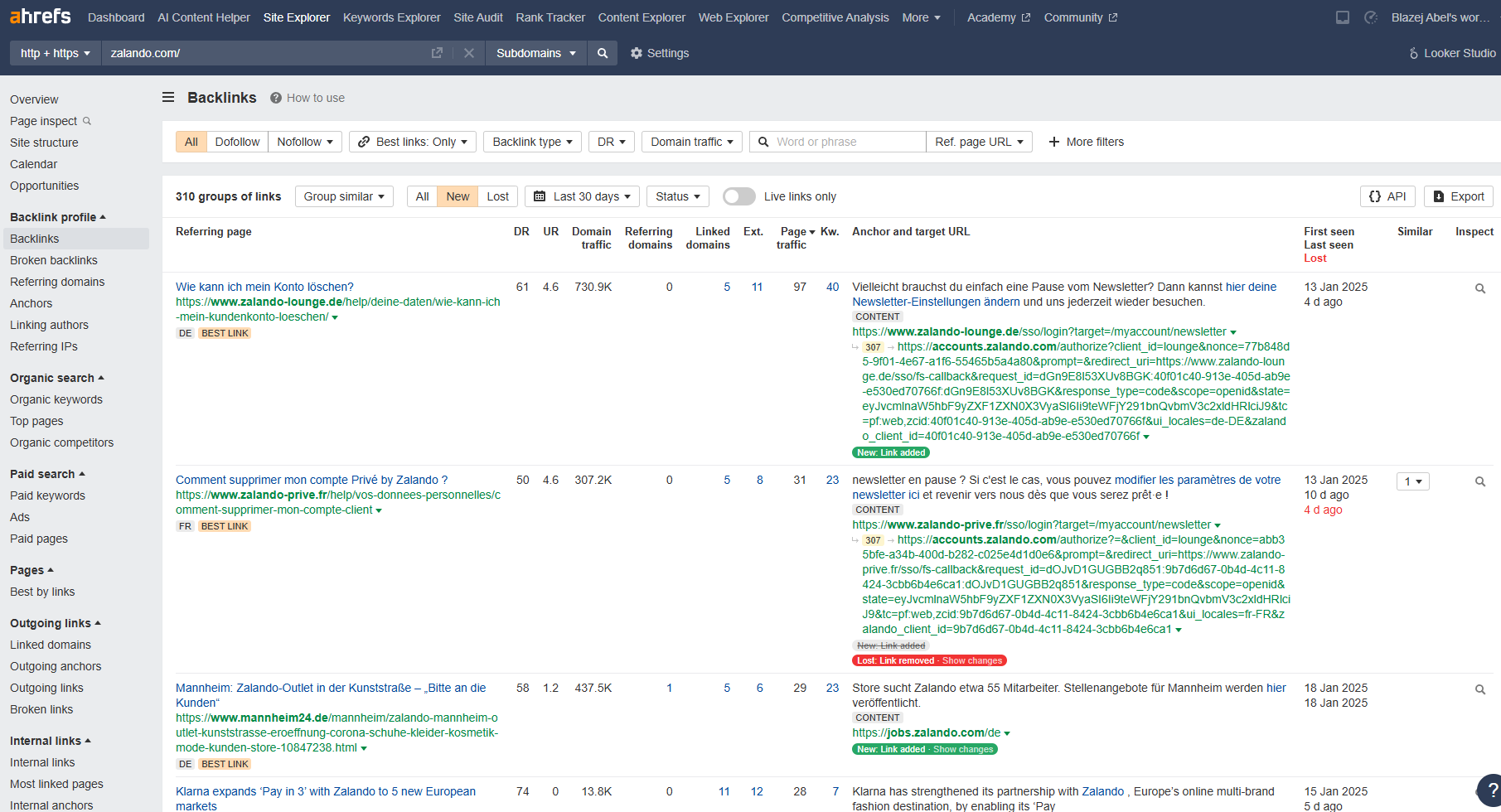
SEO tools like Ahrefs Site Explorer provide invaluable data, such as backlinks, referring domains, content performance and organic traffic insights:
- Backlinks and Referring Domains – Identify high-quality sites linking to your competitors.
Example: Competitor earns links from industry blogs like HubSpot, which you can target for guest posts or collaborations.

- Content Performance – Analyze which articles drive the most traffic.
Example: A competitor’s guide to “Best Perfumes for Summer” ranks high and attracts thousands of visitors—consider creating a better version on your blog, with better relevancy, more entities or better semantic connections than your competitor.Pro tip: If you are creating a ranking for a perfume store, mention 5 or even 10 brands. The more brands you include, the more company-type entities related to perfumes you use. This increases relevance and improves your chances of ranking higher than a competitor who mentions fewer brand entities. - Organic Search – See how much traffic competitors receive and which keywords, what pages and cover those topics.
Example: A competitor ranks for “best coffee fragrance perfumes” with high monthly search volume, so target this keyword, create your own piece of content, fill the content gap and expand your topical coverage.
c) Scrape and Group Competitor Content
Go beyond basic analysis by extracting and organizing competitor subpages to identify trends:
- Clustering by Topic – Use entities and atributes, n-gram analysis or use language models to group content into distinct topics.
- N-gram Analysis – Pinpoint recurring keyword patterns competitors use.Example: If you chose the entity relate to your brand, for example “perfume” b, go to ahrefs, than you can download all keywords that you can find in “terms match” related to perfumes, dowlnoad to google sheets and perform n-gram analysis, or you can sent this list of keywords to chatgpt or any other large language model and let him do it for you based on the spreadsheet.
d) Build a Better Topical Map
To outperform competitors, create a more comprehensive and semantically connected topical map:
- Scrape competitors pages – Extract subpages from multiple competitors.
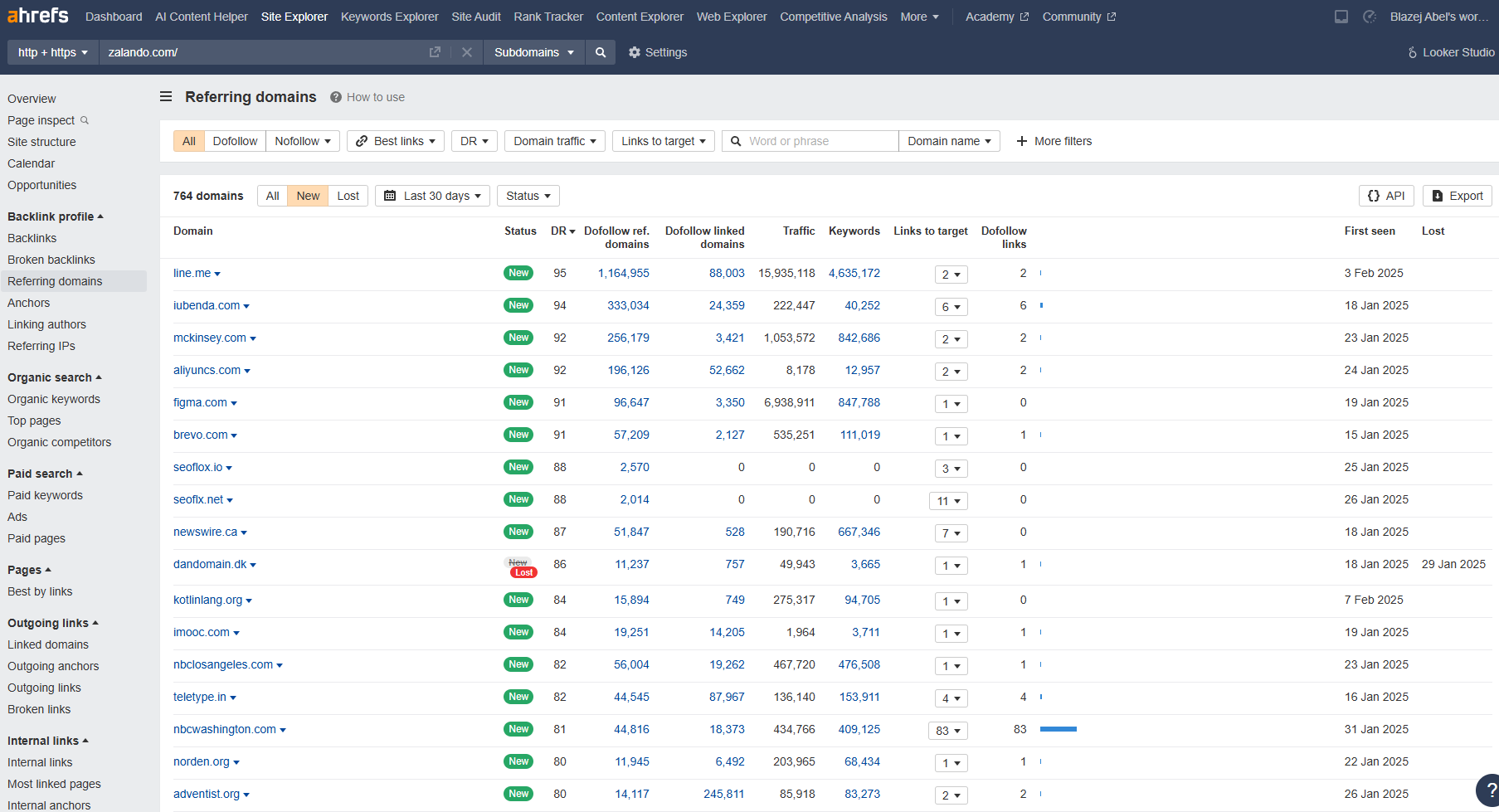
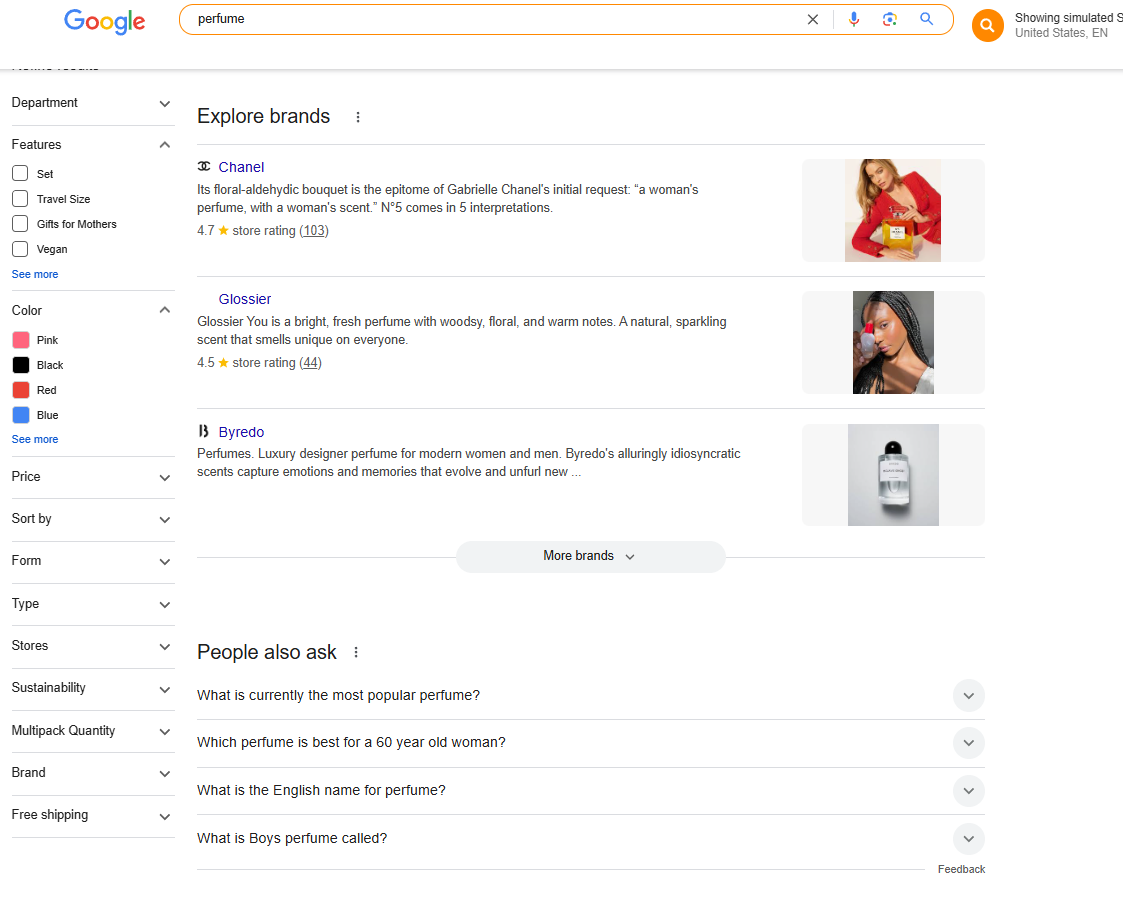
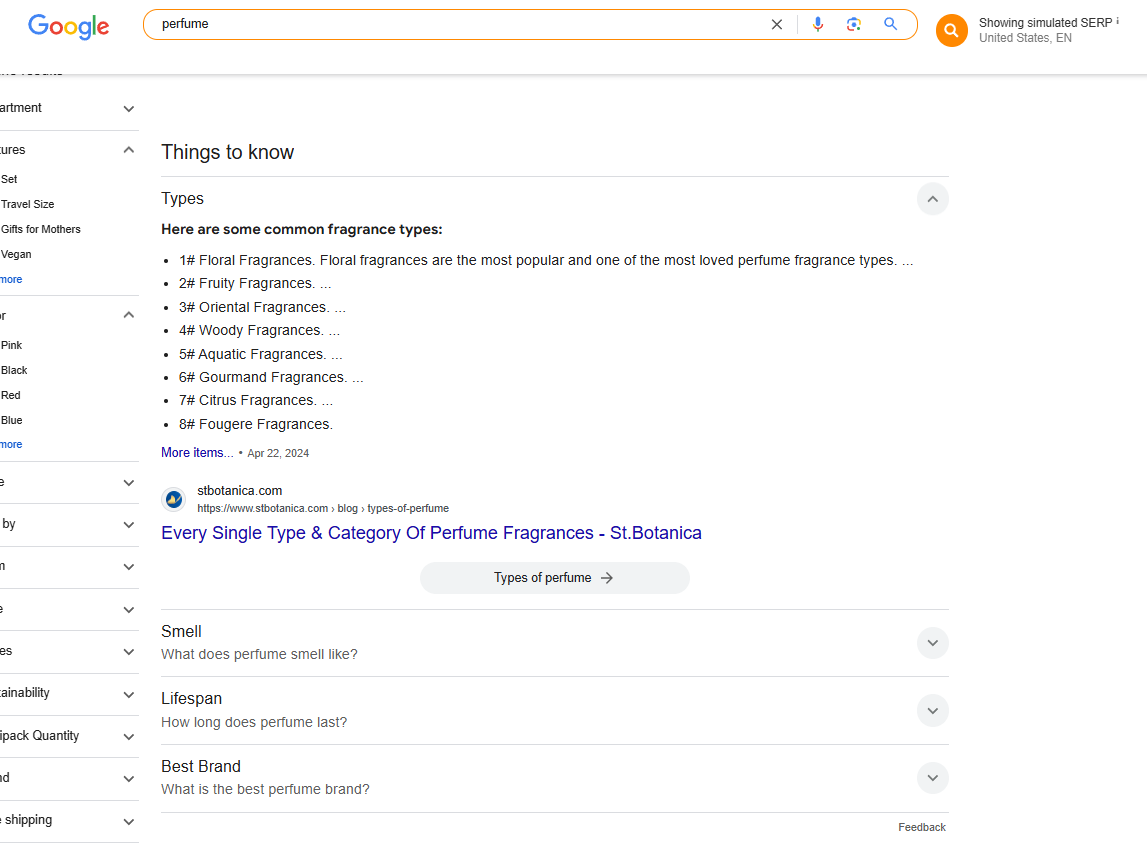
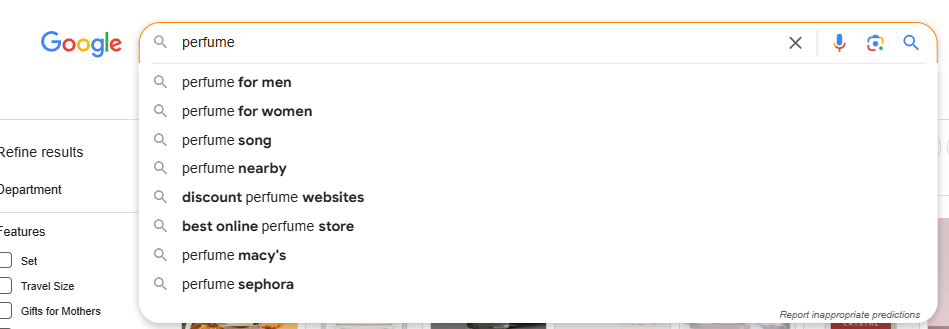
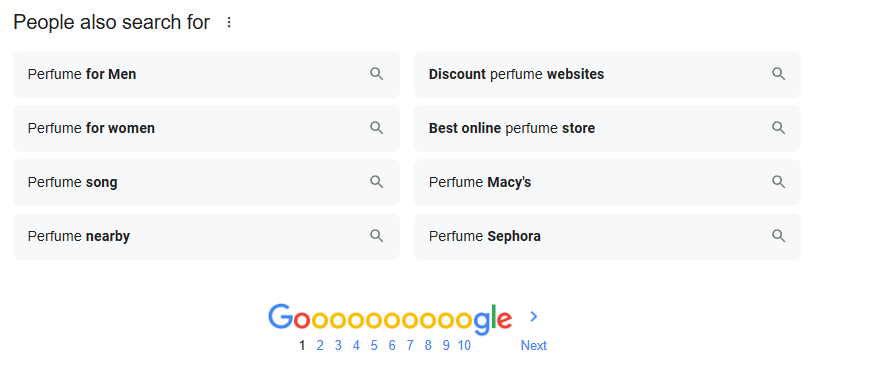
Example: Go to Ahrefs Site Explorer, enter your domain, go to the overview, and scroll down to “Top Organic Competitors.” These are competitors based on shared ranking keywords. Then, return to Site Explorer, enter their domain names, and analyze every page related to “perfume.” Collect this data in an Excel sheet, filter the topics, and create a more comprehensive topical map in your spreadsheet. - Cluster Keywords – Use SERP features like “Search suggestions”, “People Also Ask,” “People Also Search For,” and autocomplete suggestions to group related queries.
Example: Type “perfume” in the search bar and check the search suggestions. Scroll down to the “People Also Ask” section to see related topics. Then, check the “People Also Searched For” section to analyze how Google organizes these topics. - Enhance Content Coverage – Fill gaps competitors neglect.
Example: If two competitors are not covering the topic “lilac scented perfume” and only one competitor is, you have an advantage over the first two. Target this gap to improve your topical coverage.
Key Benefits of competitor analysis:
- Publish Better Content – Create more structured, in-depth articles that outperform competitors.
Example: If a competitor provides 3 statistics in their article, add 4 to yours. If they include 3 infographics, add 4. If they use only one measurement unit, use 2. (The number of words is not a ranking signal). - Identify Gaps – Spot overlooked topics to gain an edge.
- Strengthen Topical Authority – Build a robust, interlinked content strategy.
Example: Develop a topic cluster around “perfumes” with articles on perfume types, perfume rankings or history of perfumes.
2. Perform Keyword Research
Keyword research in E commerce is the process of finding and analyzing search terms that people enter into search engines with the goal of using that data for a specific purpose, often for search engine optimization (SEO) or general marketing.
Keyword analysis goes beyond identifying popular phrases—it’s about understanding their meaning, intent, and semantic connections to create highly relevant and effective content.
Instead of focusing solely on keyword competitiveness, you can rank for any query by implementing topic maps and building topical authority. While link building supports your SEO goals, it’s not the only factor that drives success.
Understand Search Intent (The “Why” Behind Keywords)
Search intent explains what a user hopes to achieve when entering a specific query. Analyzing SERP (Search Engine Result Page) helps uncover this intent, guiding you to create content that perfectly aligns with user expectations.
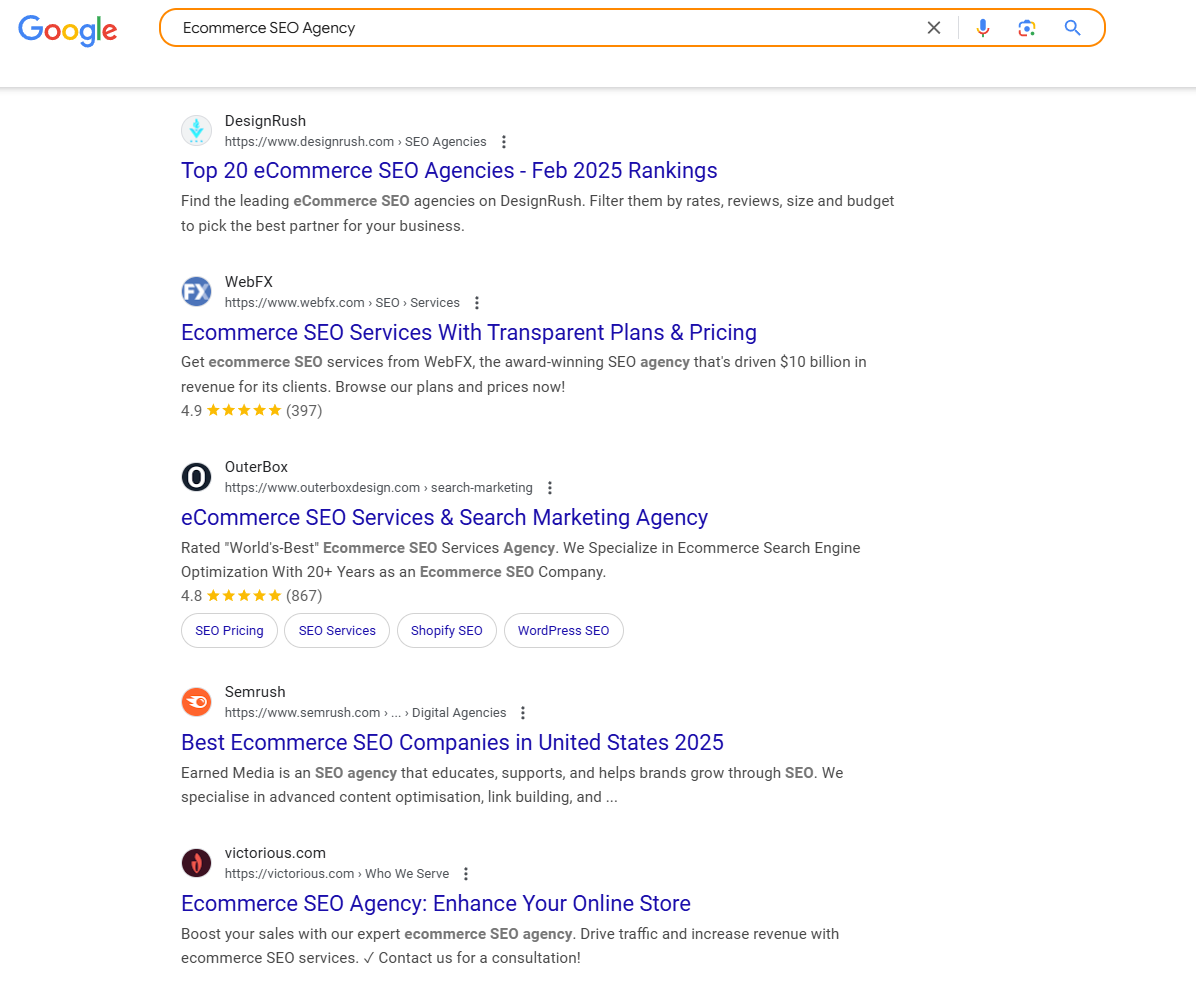
Example for “Ecommerce SEO Agency”:
- Informational Intent – Users might want a list of top marketing agencies for eCommerce SEO.
- Transactional Intent – Users are looking for specific agencies to hire, which often leads to landing pages or homepages of marketing companies.
- Localized Results – Google personalizes results based on location, browser language, or query language, often showcasing local agencies.
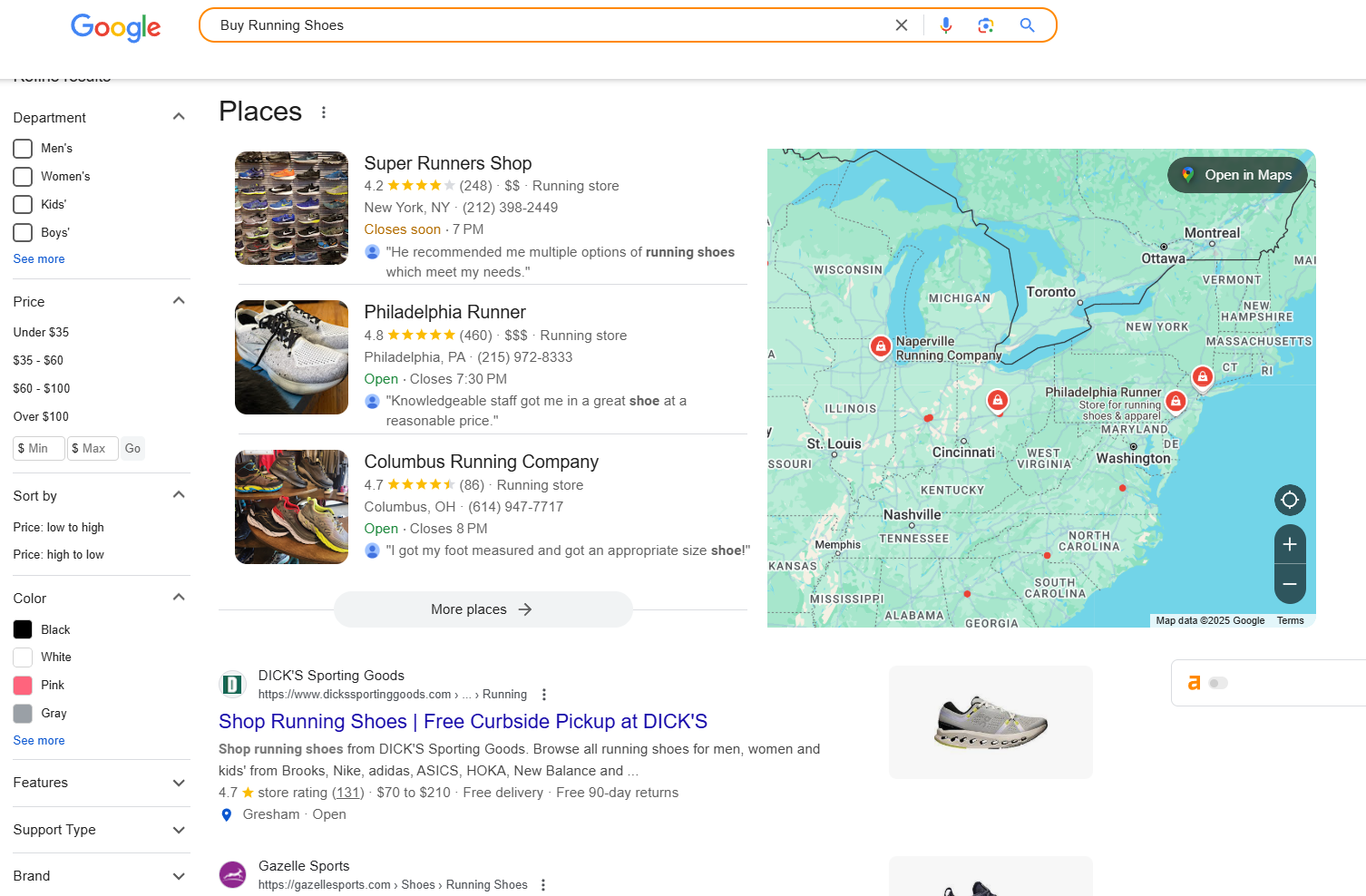
Example: For “Buy Running Shoes”:
- Informational: “Best Running Shoes for Beginners.”
- Transactional: “Buy Running Shoes Online.”
- Localized: “Running Shoe Stores Near Me.”
Use Search Volume to Structure Content
Search volume (how often a term is searched) helps determine when to create a dedicated page or consolidate related topics into a single page.
Goal: Create fewer but more comprehensive pages than competitors. Cover topics either wider (more variety) or deeper (more detail) to improve your site’s value per webpage—a metric that measures how much valuable content each page provides.
Thematic Coverage Example for “Ecommerce SEO”
Break your topic into multiple subtopics for complete coverage:
- What is Ecommerce SEO? Definition, Tips, and Examples (Pillar Page)
- Ecommerce SEO Checklist: 25 Tips
- X Best Ecommerce SEO Tools
- X Best Ecommerce SEO Agencies
- X Proven Ecommerce SEO Best Practices
- X Successful Ecommerce SEO Examples
If you’re on a tight budget:
- Combine related subtopics into 1–3 comprehensive articles.
- Expand later by creating detailed, separate articles as your resources grow.
Expert Insights for Better Results
- Balance Breadth and Depth: Cover topics extensively or deeply based on your domain’s SEO potential.
- Optimize for Semantic Relationships: Use entities (topics and concepts) and attributes (specific details) to build a robust content structure.
- Match Content to Search Engines: Understand how search engines work and adjust content strategy to align with your domain’s authority and rankability.
By mastering keyword intent, leveraging search volume insights, and building topic maps, you’ll achieve higher rankings and create a better user experience.
3. Create Information Architecture
Building a strong information architecture ensures that PageRank (or “link juice”) is distributed effectively across your website’s pages. The goal is to direct the highest value to critical pages, such as:
- Pillar Pages: Broad, foundational content.
- High-Quality Pages: Content-rich with statistics, infographics, and videos.
- Money Pages: Pages that generate revenue or lead to conversions.
Key Elements for PageRank Distribution
- Navigation Structure:
- The header menu, footer links, and homepage have the most influence on distributing PageRank.
- Well-linked pages not only gain SEO value but also improve indexing by search engines.
- URL Structure:
- Clear and descriptive URLs improve both SEO rankings and user experience.
- Good URLs should reflect the site hierarchy and include relevant keywords.
- Avoid using: capital letters, special characters, diacritical marks, underscores “_” as separators.
Examples of urls for Product Pages:
- Good URL: example.com/category/subcategory/product
- Bad URL: example.com/shop/product-name/
Examples of urls for Blog Pages:
- Good URL: example.com/lead-generation/tips
- Bad URL: example.com/22-must-know-lead-generation-tips
Why URL Structure Matters
Search engines prioritize URLs when analyzing a site’s sitemap. Intuitive URLs support internal linking and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your pages, boosting visibility in search results.
Pro Tips for Optimizing Information Architecture
- Avoid Linking Low-Value Pages:
- Pages like privacy policies or cookie notices shouldn’t appear in primary navigation.
- Combine these into one page when possible to minimize their impact on PageRank.
- Focus SEO Value on Key Sections:
- Prioritize linking to pages that align with your business goals and strategy.
- Simplify Your Sitemap:
- Keep it clear and focused, helping both users and search engine bots understand your site structure.
By aligning information architecture with SEO best practices, you enhance your website’s visibility, improve user experience, and drive more traffic to the most important pages.
4. Improve Internal linking
Internal linking is a fundamental SEO strategy that helps both users and search engines navigate your site’s structure effectively. By facilitating the flow of SEO value between pages, internal links strengthen semantic connections across your content and direct search engines to the most important sections of your website, improving their visibility in search results.
Pages with multiple internal links are often prioritized by search engine crawlers, leading to more frequent crawling and efficient indexing. To optimize internal linking, ensure anchor texts are precise, highly relevant to the linked page, and seamlessly integrated into the surrounding content.
Example of Internal Linking in a Perfume Store:
For instance, if a blog post discusses “The Best Fragrances for Summer,” you could include an internal link with anchor text like “refreshing citrus perfumes” that directs readers to the category page showcasing citrus-based perfumes. This approach not only enhances user experience by guiding them to relevant products but also helps search engines understand the relationship between your content and product pages.
You can create links from this article to specific perfumes, make sure to link them as well in introduction section.
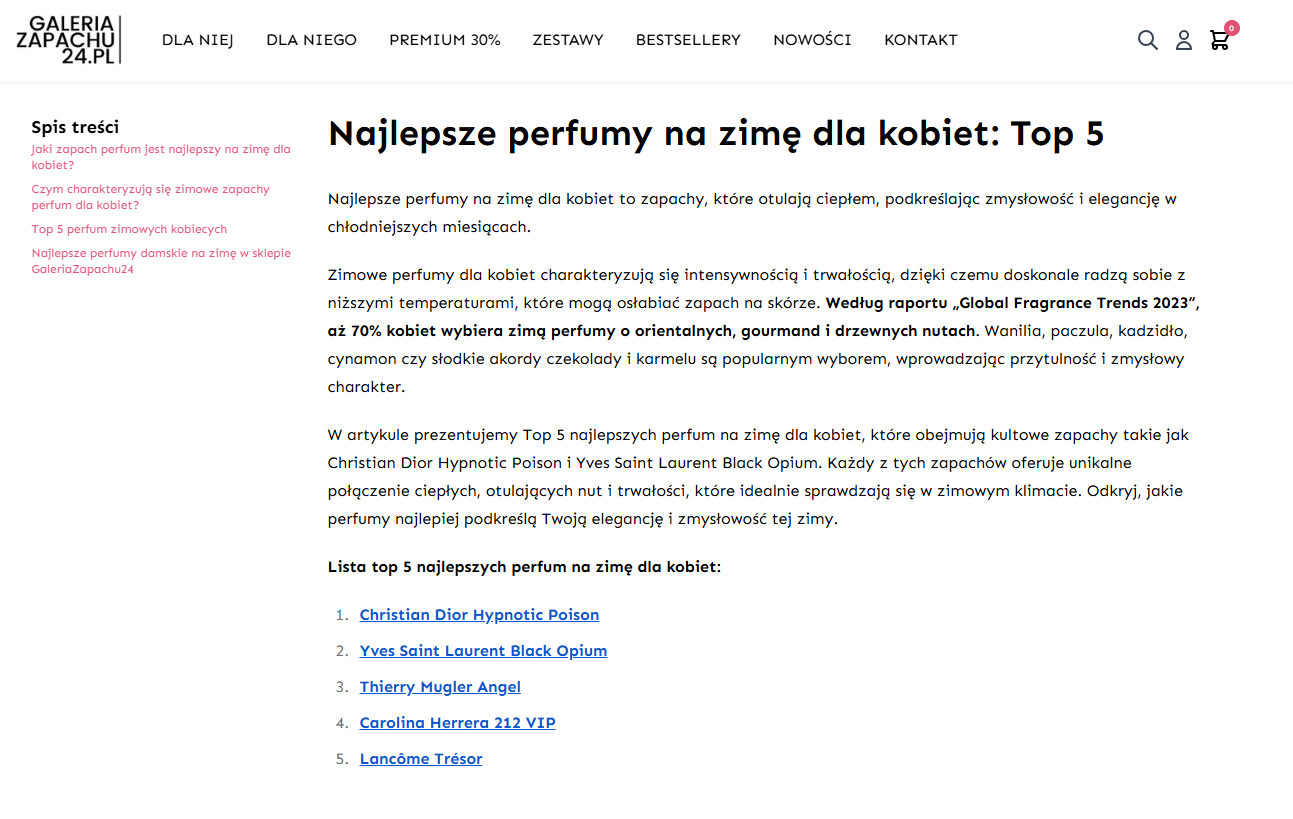
5. Create Topical Map
Creating an effective strategy for topical maps is essential for achieving e-commerce SEO success. Before developing these maps, you must identify the key topics to include. These should be semantically connected, address areas covered by competitors, and be prioritized for content creation. It’s crucial to balance topics that directly contribute to monetization with those that help accumulate valuable historical data, which is essential for becoming a topical authority in search engines and securing top positions in Google search results.
Example for a Perfume Store:
Start by covering foundational topics tied to the central entity, such as perfumes. Once these core topics are well-developed, expand into related areas, including fragrance families, atomizers, bottle design, base oils, alcohol types, essential oils, spices, and more.
This structured approach ensures your topical map supports both revenue generation and the establishment of authority, enhancing visibility and credibility in search engine rankings.
You can check Koray Tugberk Gubur Course for Semantic SEO and Topical Map Creation.
6. Increase Website Performance
Fast-loading websites are crucial for e-commerce success. Optimized performance not only increases sales but also ensures search engines can crawl your site efficiently with minimal resource usage.
According to Google, reducing load time by just 0.1 seconds can lower bounce rates by 5.7% and boost conversions by 8.4%.
Faster sites mean better user experience and higher profits!
Example: You can go to your search console, go to the settings and indexing report and you will find average response time metric.
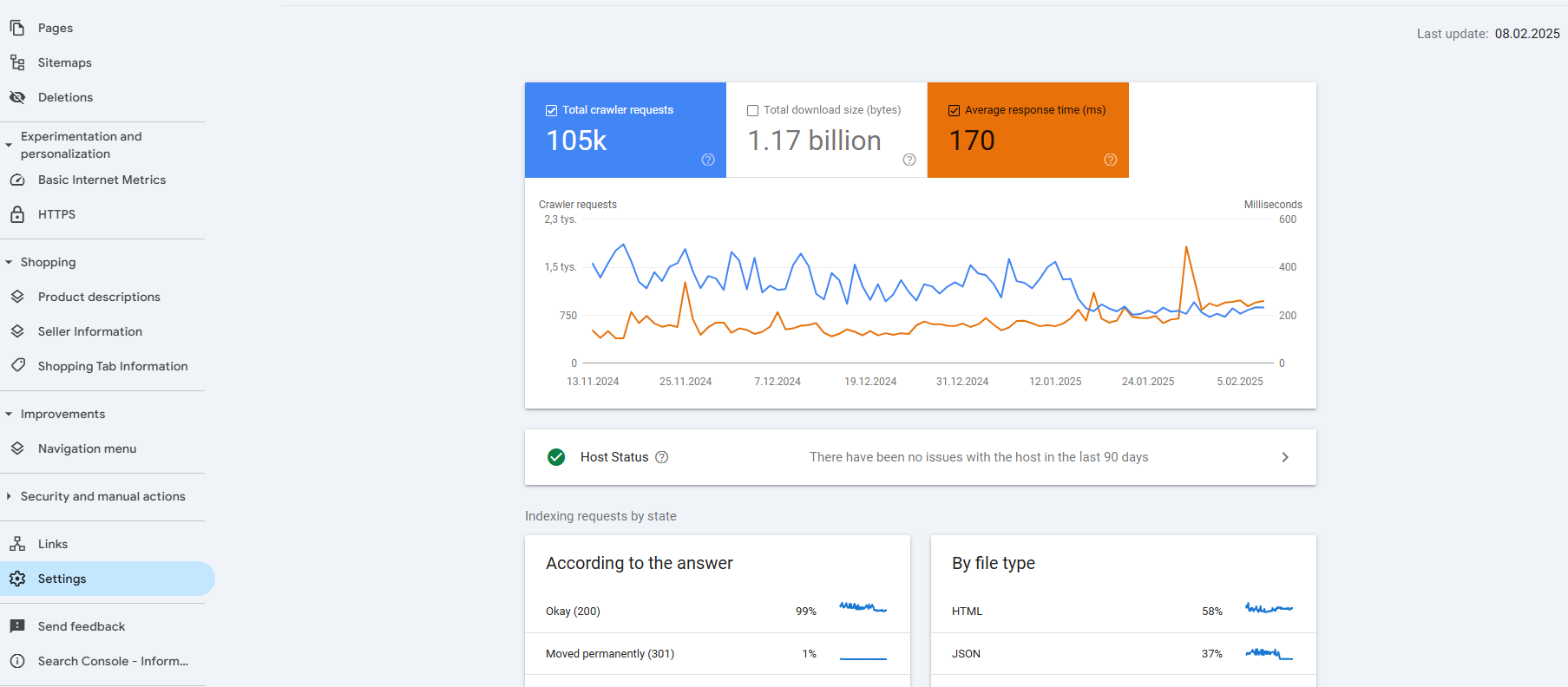
source: https://buildinmood.pl/
7. Implement Mobile Friendlies
Ensuring that your online store is mobile-friendly is essential in ecommerce SEO. This includes not just responsiveness (adjusting to various screen sizes) but also providing an exceptional user experience (UX) tailored to mobile users.
Analyze Your Audience
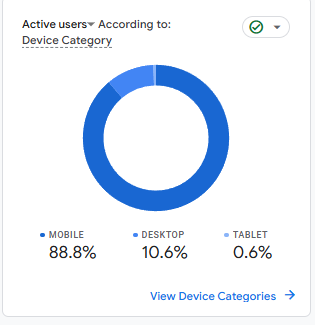
Use tools like Google Analytics, Clarity, or Piwik to identify which devices (mobile, desktop, tablet) your audience uses most.
Example 1: Perfume Store
Data from Google Analytics shows that 80% of customers for an online perfume store use mobile devices. In this case, focus on:
- Optimizing your site for mobile performance.
- Designing a mobile-friendly UX that prioritizes ease of navigation and faster checkouts.

Example 2: B2B Manufacturing Store
If your audience consists of businesses (e.g., heavy equipment buyers), the data might show higher desktop usage. For a B2B store, focus on:
- Optimizing for desktops to meet the preferences of your business audience.
- Ensuring detailed product information and advanced search options for professional users.

Benefits of PWA in E-commerce
- Faster loading times boost customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
- Offline functionality keeps your store accessible at all times.
- Push notifications increase engagement and drive repeat sales.
By tailoring your e-commerce store to your audience’s device preferences and leveraging modern tools like PWA, you can enhance user satisfaction, increase conversions, and gain a competitive edge.
8. Improve On-site SEO
Boost the performance of your product pages, category pages, homepage, blog posts, “About Us” page, and all linked subpages by optimizing their content. Create a consistent tone of voice across all pages, ensuring it aligns with your brand identity and resonates with your audience.
Maximize Product Page Effectiveness
Focus on crafting compelling product descriptions that highlight key features and unique attributes. Include essential details such as price, brand name, fragrance characteristics, scent notes, perfume concentration, longevity, bottle description, target audience, usage tips, creator information, seasonality, and occasions. This level of detail ensures your audience finds all relevant information effortlessly. Internal linking within product descriptions, like linking “bergamot” in a fragrance note to a category page featuring bergamot perfumes, enhances navigation and relevance.
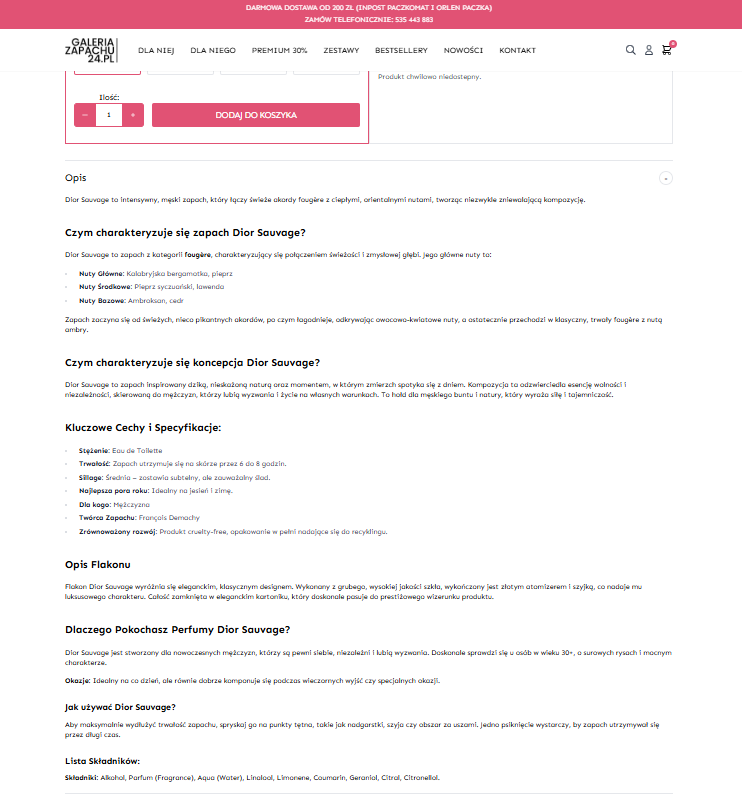
Optimize Blog Content for Engagement and Conversion
Structure blog posts in a conversational style by incorporating questions and direct answers. Use numerical lists like “10 Best Perfume Application Tips for Women” instead of general statements to capture reader attention. Integrate data, statistics, or units to enhance credibility and demonstrate expertise. Address questions succinctly at the start, then expand with examples and perspectives. Avoid vague responses like “it depends,” and provide clear answers upfront.
By optimizing these areas, you create a seamless user experience and significantly improve your site’s visibility, engagement, and conversion rates.
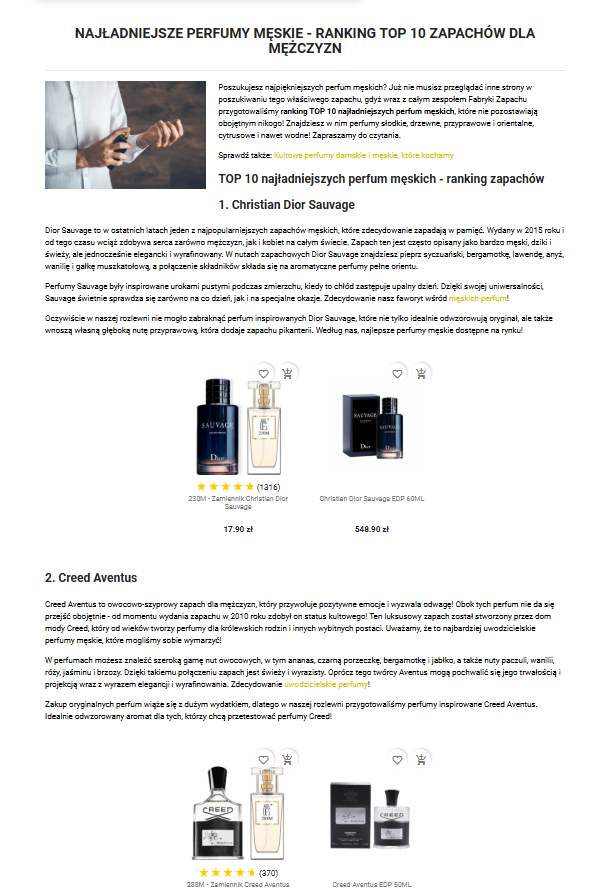
9. Create Link Building Strategy
Link building is crucial for ecommerce seo, it is your 30% of success in increasing your sales. You can help google with trusting your website or build an entity for your ecommerce site with publishing PR publications and blog posts on external websites.
Link building is a method that is creating a kind of shield that is protecting you from negative core update effects.
This is also a benefit for improving E-E-A-T for your article.
10. Implementing Structured Data
Structured data implementation allows search engines to better understand unstructured content with less computational effort and fewer algorithms. By “less effort,” we mean requiring reduced processing power, which aligns with Google’s business model of delivering high-quality search results at minimal cost.
Use Product structured data for product pages and Carousel structured data for product category pages to enhance your site’s visibility and performance in search results.
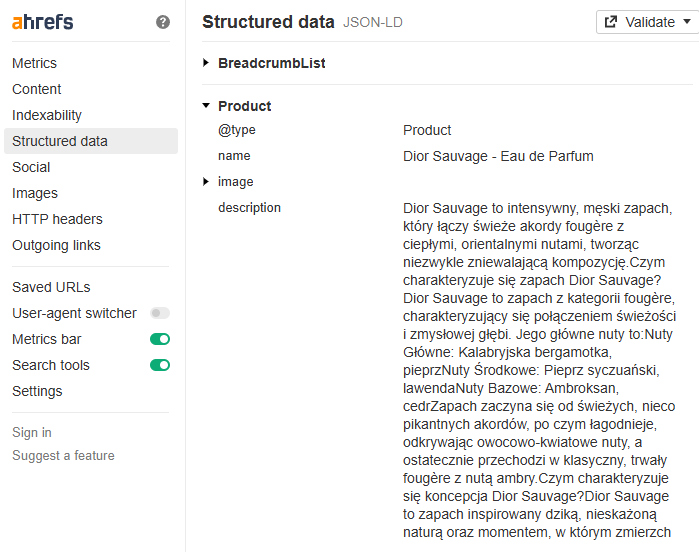
11. Use Local SEO
Optimize your ecommerce store with local SEO by incorporating location-specific keywords into your product-related queries.
If tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush indicate demand for terms like “Perfume Store near me”, identify the associated locations and target those markets, especially if you sell globally.
Boost Local Visibility:
- Gather customer reviews on your Google My Business (GMB) profile.
- Regularly publish posts and offers in GMB to engage local audiences.
Keyword Strategy for GMB:
Adjust your keywords to reflect your niche. For a perfume store, use terms like fragrance, notes, essence, or scents. If your brand is new, consider incorporating relevant keywords into your brand name for better discoverability.
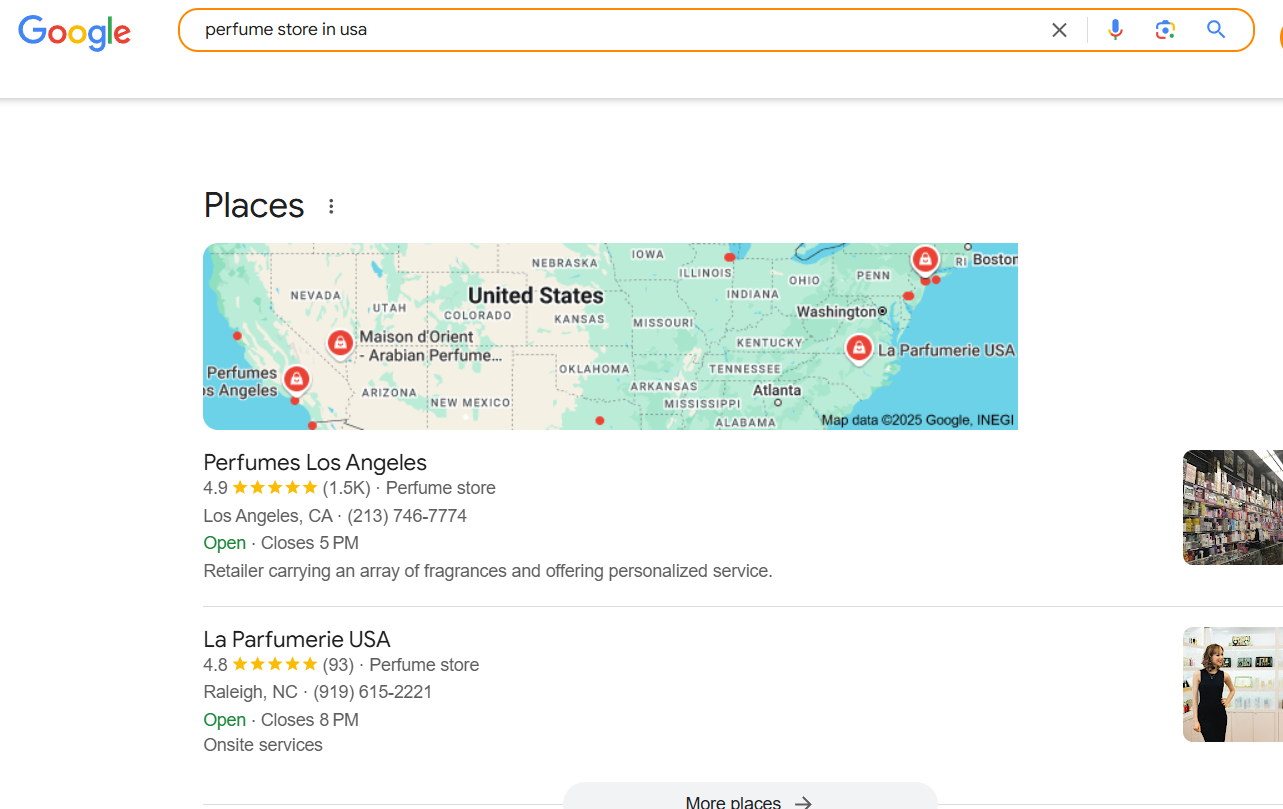
Optimize your ecommerce store with local SEO by incorporating location-specific keywords into your product-related queries. For example:
- Perfume Store Los Angeles
- Perfume Store Madrid
- Perfume Store Berlin
- Perfume Store Warsaw
- Perfume Store Paris

If tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush indicate demand for terms like “Perfume Store near me”, identify the associated locations and target those markets, especially if you sell globally.
Boost Local Visibility:
- Gather customer reviews on your Google My Business (GMB) profile.
- Regularly publish posts and offers to engage local audiences.
Keyword Strategy for GMB:
Adjust your keywords to reflect your niche. For a perfume store, use terms like fragrance, notes, essence, or scents. If your brand is new, consider incorporating relevant keywords into your brand name for better discoverability.
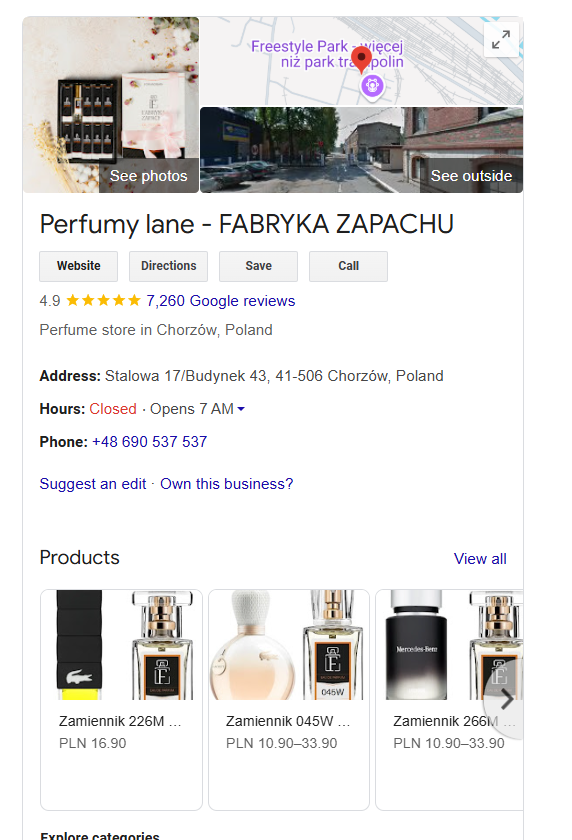
You can also add your products to GMB profile, not many brands are doing it.
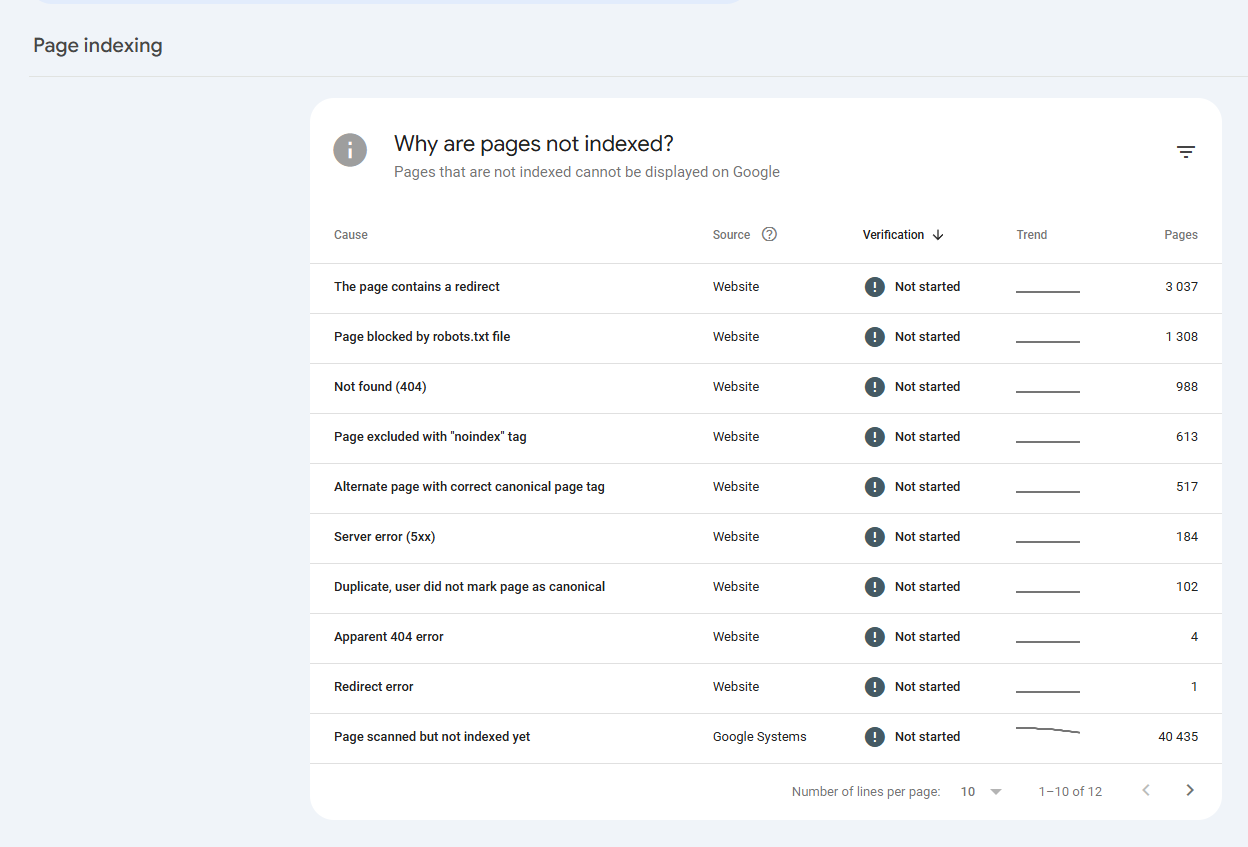
12. Fix Ecommerce Search Console Issues
Fixing Google Search Console issues in an ecommerce website means resolving errors and warnings that can negatively impact search rankings, indexation, and overall site performance. Addressing these issues ensures that search engines can properly crawl, index, and rank your pages, leading to better organic visibility.
Most Common Search Console Issues include:
- Alternate page with a proper canonical tag
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical
- Server error (5xx)
- Page excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
- Page crawled but not indexed yet
- Page discovered but not currently indexed
- Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical than user
These issues impact how Google crawls, indexes, and ranks your site, directly affecting organic visibility, traffic, and sales.
Set your gol to decrease search console issues to 0.
How to fix search console issues?
- To fix the “Alternate page with proper canonical tag” issue, ensure the affected pages have correct canonical tags pointing to the desired canonical page, which should include a self-referencing canonical tag. If any alternate pages should be indexed, update their canonical tags, internal links, and sitemap. For pages that don’t need indexing, disallow them in robots.txt to optimize crawl budget but allow initial crawling for canonical recognition. Lastly, ensure all internal links lead to the canonical page to reinforce indexing preferences.
- To fix the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” issue, implement canonical tags on duplicate pages pointing to the preferred canonical URL. Ensure the canonical page has a self-referencing canonical tag. If appropriate, use 301 redirects to consolidate duplicates into the canonical page. Also, update sitemaps and internal links to point to the canonical URL. For unique indexing, differentiate duplicate pages’ content to add distinct value for users and search engines.
- To fix the “Server error (5xx)” issue in GSC, start by identifying affected URLs in the Page Indexing or Crawl Stats reports. Check if the issue is temporary by opening the URLs in a browser after clearing the cache. Persistent errors may require disabling faulty plugins, undoing recent server updates, or correcting .htaccess files. If these steps fail, contact your hosting provider to resolve server overload or misconfiguration. Upgrading your server or optimizing site performance may also prevent future 5xx errors.
- To fix the “Excluded by noindex tag” issue in GSC, remove the noindex tag from pages you want indexed, ensuring they are valuable and meant to appear in search results. Review the “Excluded by noindex tag” list in GSC to confirm that no important pages are unintentionally excluded. If URLs marked with noindex are in your sitemap, either remove the tag or exclude these URLs from the sitemap to avoid mixed signals. After adjustments, request indexing using the URL Inspection Tool to prompt Google to crawl and index the updated pages.
- To fix the “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” issue in Google Search Console, ensure your pages provide high-quality, unique content that aligns with user intent. Review and improve affected pages, optimizing their structure and internal linking to signal value to Google. Remove duplicate content or properly implement canonical tags to avoid confusion. Use the URL Inspection Tool to request re-crawling or create a temporary sitemap for affected URLs to prompt indexing. These actions help prioritize your valuable pages and improve indexing efficiency.
- To fix the “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed” issue, improve the quality and uniqueness of your content to meet Google’s standards and avoid duplicates. Strengthen internal linking to signal the importance of affected pages. Use robots.txt to prevent Googlebot from wasting crawl budget on low-quality pages and focus on essential content. Ensure your sitemap includes only canonical, indexable URLs and address redirect chains or server overload issues. Finally, request indexing for updated pages via the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to prioritize their crawling and indexing.
- To fix the “Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user” issue, ensure canonical tags are consistent and point to the correct URL. Check that duplicate pages reference the canonical page and remove self-referencing canonical tags from duplicates. Only include canonical URLs in your sitemap and adjust internal links to point to the preferred page. Ensure the canonical page uses HTTPS, has a 200 status code, and features a clean, human-readable URL. Finally, request re-indexing in Google Search Console to prompt Google to recognize your changes.

13. Use Multilangual and Multiregional SEO
Ecommerce Multilingual SEO involves optimizing websites for multiple languages and regions to enhance visibility and user experience across diverse linguistic and geographic markets.
Key practices include the use of consistent hreflang tags in HTML, sitemaps, and headers to signal alternate versions to search engines.
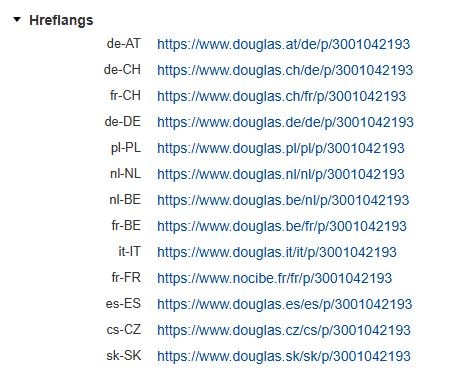
Localized content should maintain factual consistency while being culturally relevant.
Technical optimizations, such as lightweight HTML and CSS and local servers or CDNs, ensure fast load times.
A subfolder URL structure is preferred over subdomains to centralize authority.
Internal linking must uniformly connect canonical and alternate versions to balance PageRank flow.
Structured data, including localized schema markup, improves search engine comprehension.
Performance optimization, especially focusing on Core Web Vitals, is crucial for user satisfaction and search rankings.
Even if you are not selling to specific countries or regions like Indonesia you can translate part of your content to get more traffic and historical data.
Translating your website is a cost-effective and fast way to increase sales and boost global brand awareness.
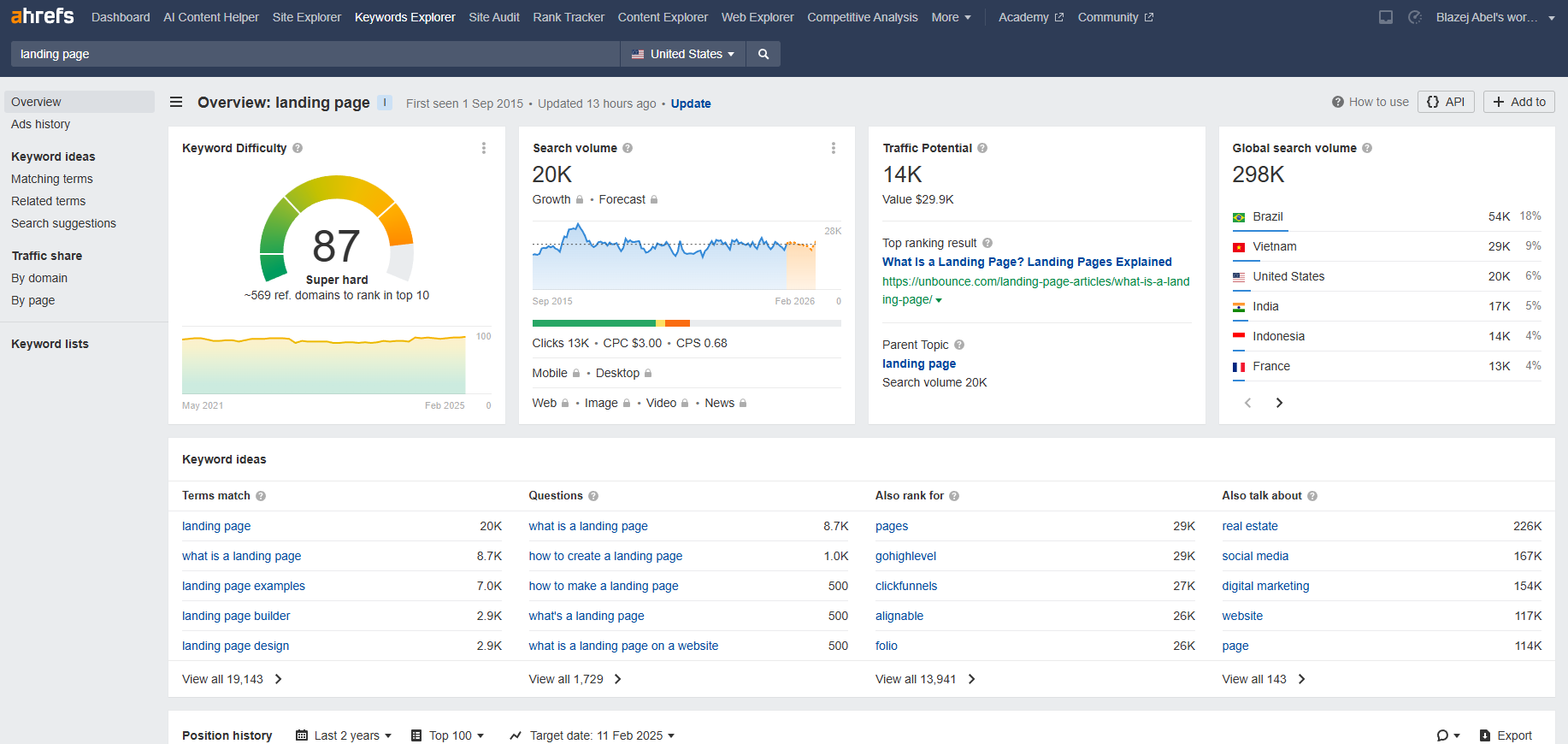
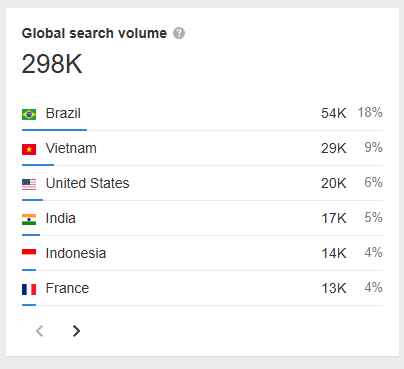
Sometimes, Google automatically translates your pages when localized search results, such as in Indonesia, lack quality content. This indicates the quality of your content and reveals niches with demand for specific queries. It also signals whether you are becoming a topical authority.
International e-commerce SEO analysis helps you outpace competitors globally while boosting visibility in your home market. Multilingual store versions generate historical search data, strengthen domain authority, and improve rankings, even if most of your sales come from one country.
Pro Tip: Go to the “Search Result” in Search Console and filter “Appearance in search engine” and then click “Translated Results”.
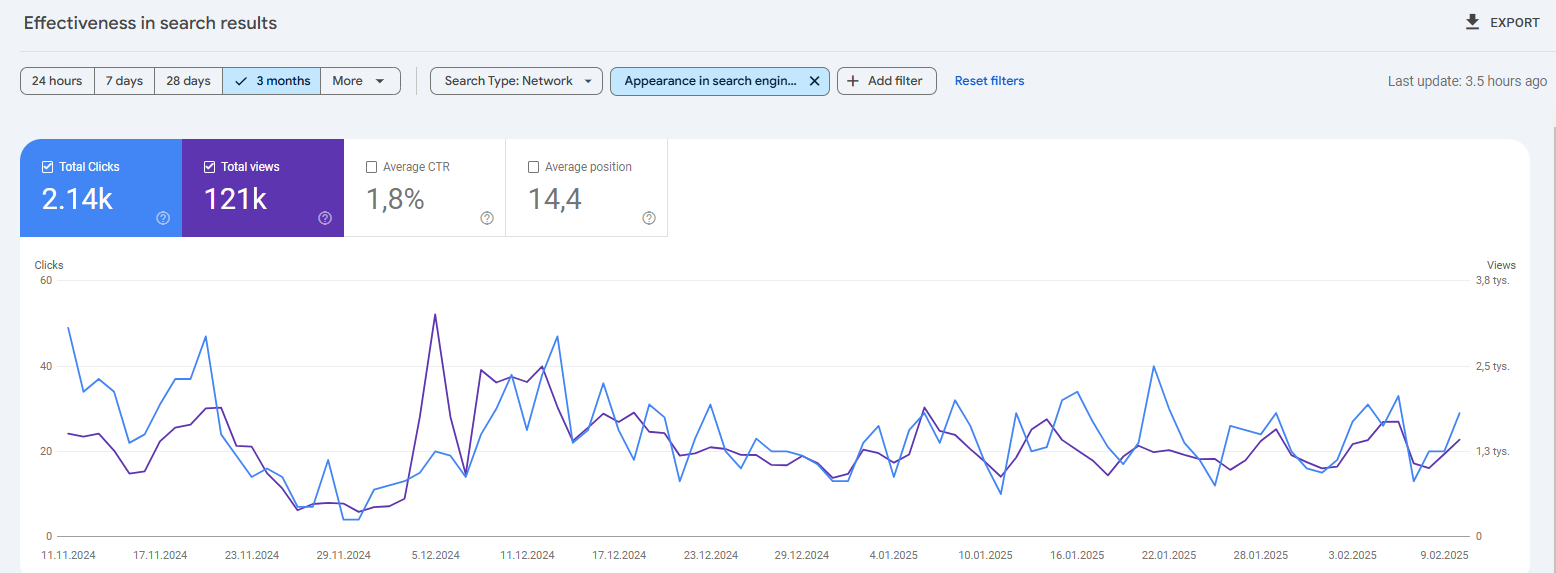
You can use Landingi to create Ecommerce landing pages in multiple languages.
14. Implement Javascript SEO
If your ecommerce website uses JavaScript frameworks like Next.js, prioritize Server-Side Rendering (SSR) over Client-Side Rendering (CSR). SSR ensures web crawlers, like Googlebot, can efficiently process your content without delays caused by rendering complexities. In contrast, CSR can lead to higher crawling costs and indexing delays, which can negatively impact your SEO performance.
Here are 5 best practices to optimize JavaScript SEO usage for ecommerce sites:
1. Avoid CSR for Critical Pages
CSR can delay the rendering of essential content, making it harder for search engines to index your pages. SSR provides pre-rendered HTML, reducing the processing load on crawlers and improving your crawl budget efficiency.
2. Beware of Hidden HTML Content
Some JavaScript frameworks fail to render HTML for elements like accordions or collapsed content within the DOM. Ensure all critical content is accessible and visible to search engines, even without user interaction.
3. Optimize Pagination
Avoid using JavaScript-only solutions for pagination unless they are SSR-based. Pagination should rely on standard HTML <a href> links, allowing search engines to discover all pages efficiently. Infinite scroll implementations should include fallback solutions like a paginated structure.
4. Monitor Renderability
Use tools like Google’s URL Inspection Tool or Lighthouse to verify that Google can render and index all critical content. Compare the raw HTML and rendered DOM to ensure no important content is missing.
5. Pre-rendering for Complex JS
For ecommerce sites with extensive JavaScript use, consider dynamic rendering or hybrid rendering techniques for pages with heavy reliance on JavaScript. This helps ensure that search engines can index dynamic content effectively.
15. SGE – Search Generative Experience Optimization
Google’s Search Generative Experiences (SGE) transforms how search results are created, prioritizing AI-driven content generation over traditional link-based results.
To ensure your e-commerce site remains competitive, focus on building a presence in platforms that feed AI models, such as Reddit, Quora, and other community-based websites.
Actively engage by answering questions and subtly referencing your store and products to increase visibility in SGE-driven recommendations.
SGE favors detailed, context-rich content that aligns with user-specific queries. While traditional SEO thrives on concise keywords, SGE encourages natural, conversational content.
To optimize, strike a balance between creating content that appeals to AI preferences and traditional search engines, while always prioritizing the user’s intent.
SGE also introduces unique result formats, such as product viewers, unordered lists, and local packs, making schema markup, structured data, and detailed product descriptions essential for visibility.
Staying updated with SGE trends and adapting your content to match its evolving modules will ensure your e-commerce site remains competitive in this AI-driven search landscape.
source: https://blog.google/
16. Get reviews for your product pages
Customer reviews on product pages are crucial for eCommerce SEO. They not only enhance trust and credibility but also significantly influence your ranking in search engine results.
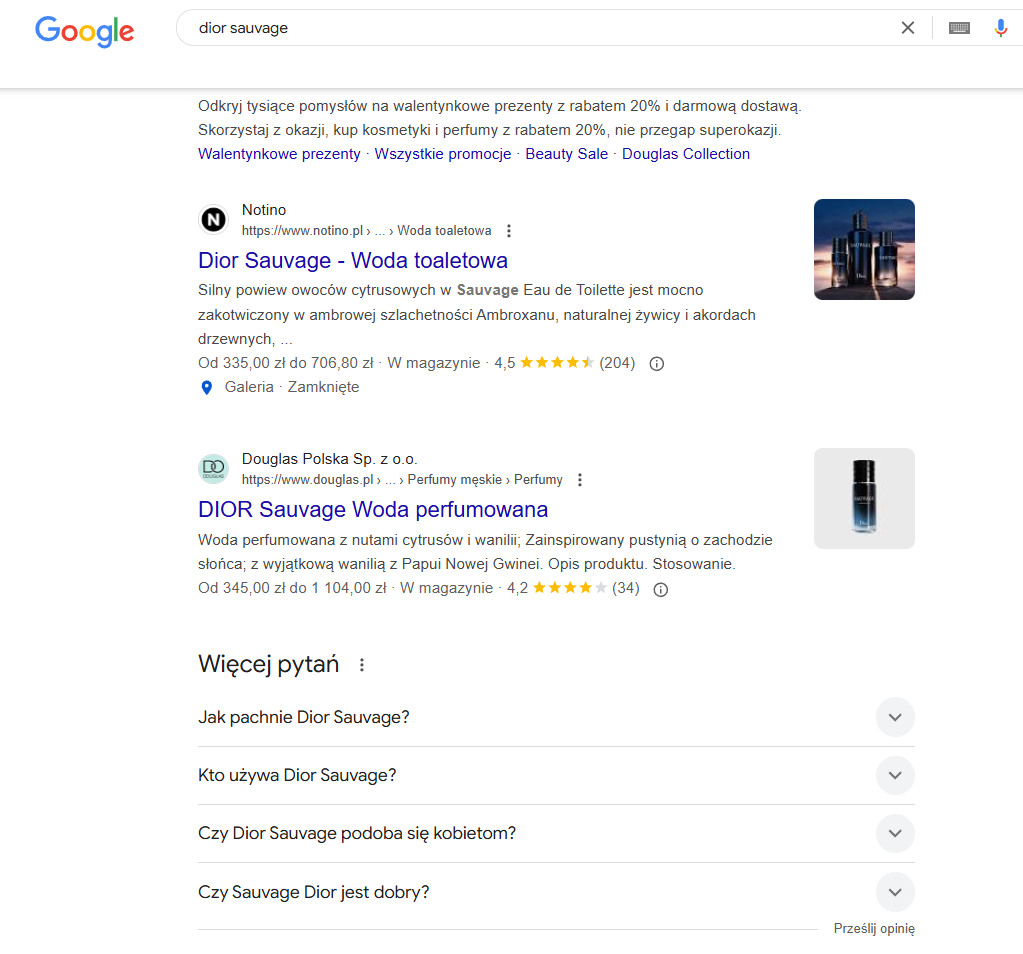
To outperform competitors, ensure your product pages gather more high-quality reviews than theirs.
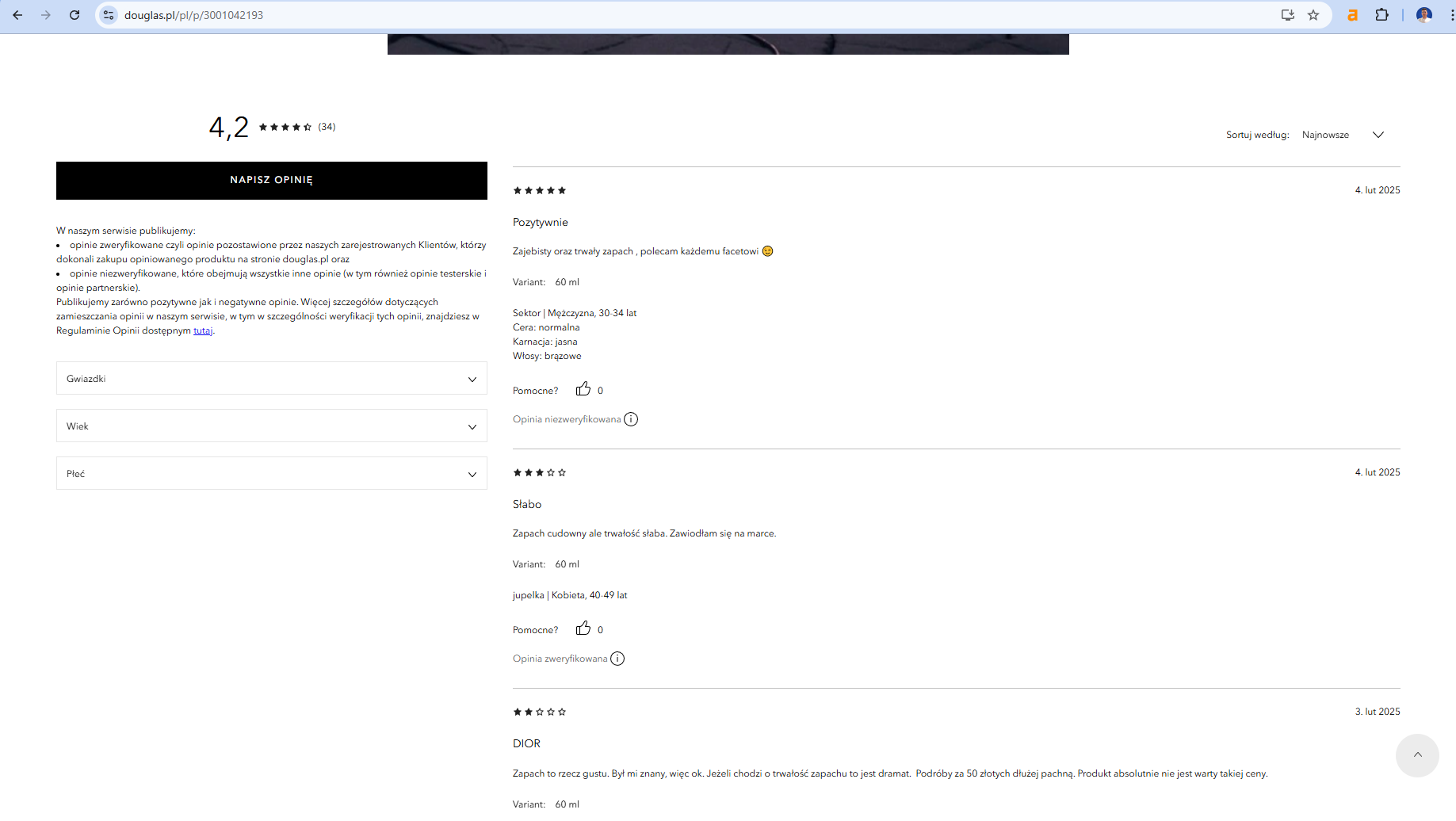
Additionally, reviews should reflect the same sentiment as those on other platforms to maintain consistency and authenticity.
Incorporate structured data markup for reviews, enabling rich snippets that increase your click-through rate (CTR) in search engine results pages (SERPs).
FAQ – Ecommerce SEO Tips
What’s the importance of landing pages in ecommerce SEO?
Landing pages play a crucial role in e-commerce SEO by improving conversions and search engine visibility. They are optimized for specific keywords and user intent, enhancing rankings in SERPs and attracting high-value traffic.
Additionally, well-structured landing pages enhance user experience by eliminating distractions and guiding visitors directly toward a purchase. They also serve as effective lead generation tools through sign-up forms and special offers. A/B testing helps optimize their performance, while user behavior analysis provides valuable insights for refining marketing strategies. Lastly, organic traffic from landing pages is more cost-effective in the long run than paid advertising, making them a key component of any e-commerce SEO strategy.
How is ecommerce SEO different from other types of SEO?
E-commerce SEO differs from traditional SEO by focusing on product-specific optimization, high-purchase-intent keywords, and conversion-driven strategies. It prioritizes long-tail commercial keywords, optimized product and category pages, and structured data to improve product discoverability.
Additionally, e-commerce SEO places strong emphasis on technical aspects such as site architecture, fast loading times, and user experience to streamline the shopping journey and reduce cart abandonment. Unlike traditional SEO, which often centers on informational content and brand authority, e-commerce SEO is designed to drive direct sales and optimize the entire purchase funnel.
How to find keywords for an ecommerce website?
To find keywords for an e-commerce website, start by analyzing competitors using tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to identify high-ranking keywords and gaps in your strategy. Use Google Autocomplete to discover long-tail keywords based on real user searches.
Leverage ecommerce keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, Keywords Everywhere, and Ubersuggest to gather search volume, competition, and cost-per-click data. Prioritize transactional keywords that indicate purchase intent, such as “buy running shoes online.” Additionally, analyze customer feedback, surveys, and social media comments to find natural language terms used by buyers.
Refine your keyword list by focusing on relevance, search volume, and competition level. Finally, monitor trends with Google Trends to adjust for seasonal changes and emerging interests, ensuring your keyword strategy remains competitive and effective.
What is the best tool for ecommerce SEO?
The best tool for e-commerce SEO depends on your specific needs. SEMrush and Ahrefs are top choices for comprehensive SEO management, offering ecommerce keyword research, competitor analysis, and site audits.
For Shopify users, ConvertMate provides automated meta tag and product description optimization. Ubersuggest is user-friendly option for keyword research without buget. Screaming Frog excels in technical SEO audits, while SEO Review Tools and SEOquake offer free solutions for backlink and SERP analysis.
Choosing the right tool depends on your store size, budget, and specific SEO priorities.
How to learn e-commerce SEO?
To learn e-commerce SEO, start with the fundamentals by understanding search engine mechanics, keyword research, and on-page and technical SEO. Use beginner-friendly resources like Ahrefs blog and youtube tutorials from Matt Digitty or Koray Tugberk Gubur blue hat series.
Next, focus on e-commerce-specific strategies, such as optimizing product pages, implementing schema markup, and improving site structure. Guides from Onely and Search Engine Journal provide comprehensive insights. Use tools like Ahrefs to research long-tail keywords with high purchase intent.
Implement on-page SEO by optimizing meta tags, descriptions, and content structure (H1, H2, H3). Ensure your site is technically sound by improving speed, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS security. Develop backlinks through guest blogging and influencer outreach.
Monitor performance using Google Analytics and Search Console while staying updated with SEO trends via Moz, HubSpot, and SEMrush blogs. Consider structured learning through Coursera or Udemy courses, and gain practical experience by optimizing your own or a small business’s e-commerce site.
What is the best SEO course for ecommerce?
The best SEO course for e-commerce is Koray Tugberk Gübür’s Topical Authority Course. Koray is a recognized expert in semantic SEO, and his course provides a unique approach to building topical authority, which is essential for long-term success in search rankings.
Unlike traditional SEO courses that focus primarily on keyword research and technical optimization, Koray’s course teaches how to establish authority in a niche through advanced topical mapping, content structuring, and semantic SEO strategies. This approach allows e-commerce websites to achieve sustainable rankings and generate consistent organic traffic.
Other courses, such as HubSpot Academy, Yoast, Semrush Academy, and Udemy, offer strong foundations in SEO and technical optimization. However, Koray’s course stands out by providing a strategic, data-driven method to dominate search results in competitive markets. If you want to gain a competitive edge in e-commerce SEO, this is the best course to invest in.
Which ecommerce platform is best for SEO?
The best e-commerce platform for SEO is Next.js, thanks to its server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), and full control over technical SEO. Unlike traditional platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce, Next.js ensures faster page loading, better Core Web Vitals, and advanced customization for search engine optimization.
However, the right choice depends on your needs:
- Ease of use: Shopify is best for beginners, offering built-in SEO tools without coding.
- Content marketing & flexibility: WooCommerce (WordPress) provides deep SEO customization and access to plugins like RankMath (I recommend Flatsome templates for WordPress, because they are lightweight).
- Enterprise-level SEO: BigCommerce and Magento are great for large stores requiring advanced technical SEO features.
- Speed & performance: Next.js dominates in site speed, structured data implementation, and dynamic routing, making it ideal for scalable, high-performance e-commerce SEO.
- Budget & customization: PrestaShop and Wix eCommerce offer free or low-cost solutions but lack advanced optimization options.
If you want the best performance, Core Web Vitals optimization, and complete SEO control, Next.js is the ultimate choice for e-commerce SEO. However, if you prefer an out-of-the-box solution, Shopify or WooCommerce may be better suited.
Where to find the best ecommerce SEO services?
The best place to find e-commerce SEO services is by working with talented freelancers who offer personalized, cost-effective, and highly specialized solutions. Unlike agencies, freelancers can provide dedicated attention, flexible pricing, and customized strategies tailored to your business needs.
However, if you prefer working with an SEO agency, here are some top companies recognized for their expertise in e-commerce SEO:
- Thrive Internet Marketing Agency – Offers full-service SEO with a focus on conversions.
- WebFX – Data-driven strategies for improving search rankings and increasing sales.
- Infidigit – Specializes in technical SEO and content optimization for e-commerce.
- OuterBox – Provides customized SEO solutions for online retailers.
- Coalition Technologies – Known for its expertise in Shopify and Magento SEO.
While agencies have structured processes, freelancers often deliver more agility, cost savings, and direct collaboration. You can find top freelance SEO experts on platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, or LinkedIn, ensuring you get a tailored approach with expert-level execution.
For the best results, consider freelancers with proven experience in e-commerce SEO, as they can often outperform agencies in both strategy and execution while offering a more personal, hands-on approach.
How ecommerce SEO is different from normal SEO?
E-commerce SEO differs from normal SEO by focusing on product visibility, transactional keywords, and conversion-driven strategies, whereas traditional SEO is broader, targeting informational searches and brand authority.
Key Differences:
- Target Audience – E-commerce SEO targets buyers ready to purchase, while normal SEO attracts users at different stages of the buyer’s journey.
- Keyword Strategy – E-commerce SEO prioritizes long-tail, transactional keywords like “buy running shoes online,” whereas normal SEO includes informational and navigational queries.
- Content Focus – E-commerce SEO optimizes product and category pages, while normal SEO relies on blog posts and service pages for engagement.
- Technical SEO – E-commerce requires structured data, fast-loading product pages, and optimized site architecture for seamless navigation.
- Goals & Metrics – E-commerce SEO measures sales and conversions, while traditional SEO tracks engagement, brand awareness, and lead generation.
Where to find an ecommerce SEO checklist?
You can find a comprehensive e-commerce SEO checklist from the following trusted resources:
- WebFX – 2025 56-Point SEO Checklist
Covers keyword research, technical SEO, content creation, and ongoing strategies for better rankings. - NitroPack – 2024 E-commerce SEO Checklist
Focuses on on-page SEO, page structure, product images, and keyword usage to enhance site performance. - SEMrush – E-commerce SEO Checklist
Provides 22 expert tips on on-page, off-page, and technical SEO strategies for e-commerce websites.
These checklists will help you effectively optimize your e-commerce website and improve your search engine visibility.
What are the challenges of ecommerce SEO?
E-commerce SEO comes with unique challenges that can impact visibility, rankings, and conversions. The main issues include:
- Technical SEO Issues – Slow site speed, poor mobile optimization, and complex site architecture can hinder search rankings and user experience.
- Duplicate Content – Using manufacturer descriptions or having similar product pages can lead to penalties. Implementing canonical tags and creating unique product descriptions helps solve this.
- Poor User Experience (UX) – Complicated navigation and a lengthy checkout process can increase bounce rates and cart abandonment.
- Content Marketing Challenges – Balancing SEO-optimized product pages with engaging, valuable content is essential but difficult.
- High Competition – E-commerce is highly saturated, making it hard to rank for competitive keywords without continuous optimization.
- Algorithm Changes – Search engine updates require constant adaptation to avoid losing rankings.
- Analytics & Monitoring – Many businesses struggle with proper tracking and data analysis, making it hard to refine their SEO strategies.
What are the KPIs to measure ecommerce SEO success?
E-commerce SEO success is measured by organic traffic, keyword rankings, and CTR, which indicate visibility. Conversion rate and bounce rate show how well traffic turns into sales. Core Web Vitals, indexed pages, and backlinks impact rankings and user experience. Domain authority, search visibility, and CLV reflect long-term SEO value. Regular tracking ensures continuous optimization and revenue growth.
What is the cost of SEO for ecommerce?
The cost of e-commerce SEO in 2025 varies based on project complexity, competition, and services required. Monthly retainers range from $500 to $10,000+, with smaller businesses spending around $2,500–$5,000/month and larger enterprises exceeding $5,000/month. Hourly rates typically fall between $51–$300/hour, depending on the provider’s expertise and location. Project-based SEO can cost anywhere from $500 to $10,000+, with enterprise-level optimizations demanding higher budgets.
Costs are influenced by competition level, site size, and service scope. More competitive niches and larger e-commerce stores require greater investment. Choosing a quality SEO service that aligns with business goals ensures a strong return on investment.
Is there a difference in doing SEO for B2B e-commerce vs. B2C e-commerce?
Yes, SEO for B2B and B2C e-commerce differs significantly in terms of target audience, keyword strategy, content marketing, and sales cycles.
B2B e-commerce SEO focuses on decision-makers within companies, using long-tail, solution-oriented keywords with lower search volume but higher conversion potential. The content strategy is more educational, featuring whitepapers, case studies, and in-depth blog posts to nurture leads over a longer sales cycle. Link building relies on industry-related sites, trade publications, and partnerships, and the SEO goal is lead generation rather than immediate sales.
B2C e-commerce SEO, on the other hand, targets individual consumers searching for products with high-volume, purchase-driven keywords. Content is product-focused, often using reviews, lifestyle content, and promotions to drive quick sales conversions. The sales cycle is shorter, and link-building strategies involve influencers, blogs, and consumer websites.
While both require technical SEO and optimization, understanding buyer intent and search behavior is crucial for crafting the right strategy.
What are the limitations of ecommerce SEO?
E-commerce SEO faces several limitations, including technical complexity, duplicate content issues, poor user experience, content limitations, high competition, frequent algorithm changes, resource-intensive efforts, and analytics challenges.
The technical structure of large e-commerce sites can make crawling and indexing difficult, while slow loading speeds negatively impact rankings. Duplicate content, often from manufacturer descriptions, can lead to penalties, reducing visibility in search results. A complicated user experience, including hard-to-navigate categories and slow checkout processes, increases bounce rates and cart abandonment.
Creating unique, high-quality content for thousands of product pages is a major challenge, as many businesses rely on generic descriptions. The competitive nature of e-commerce makes ranking difficult, especially for smaller businesses competing against established brands. Additionally, frequent algorithm updates require constant monitoring and adjustments to SEO strategies.
E-commerce SEO is also resource-intensive, demanding continuous investments in technical optimization, content development, and link-building efforts. Tracking SEO performance across a large number of product pages further complicates optimization. To mitigate these challenges, businesses must prioritize site speed, improve content uniqueness, enhance user experience, and maintain a proactive SEO strategy.
Boost Your Ecoomerce SEO with High Converting Landing Pages
E-commerce SEO is a powerful strategy for increasing visibility, driving organic traffic, and improving conversion rates. By implementing technical optimizations, keyword research, content marketing, and user experience enhancements, online stores can outperform competitors and establish long-term success.
The key to sustained growth lies in building topical authority, optimizing product pages, improving site speed, and leveraging structured data to enhance search rankings. Businesses that prioritize SEO can reduce customer acquisition costs, increase brand trust, and generate consistent sales without relying solely on paid advertising.
Real-world success stories show that effective e-commerce SEO strategies lead to higher search engine rankings, improved customer engagement, and better revenue growth. By staying ahead of search engine updates and continuously refining your SEO efforts, you can dominate the digital marketplace.
A well-optimized landing page is the foundation of any successful e-commerce SEO strategy. Enhance your conversions, improve user engagement, and drive more sales with professionally designed, SEO-friendly landing pages.
Try Landingi for free and build high-converting pages that turn visitors into customers!